| Clone | QR043 |
|---|---|
| REF | C-N001 |
| Dilution | 1:100 – 1:200 |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human NUT |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Species of origin | Rabbit |
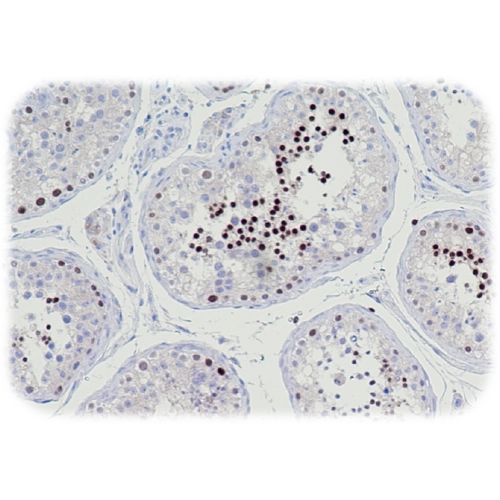
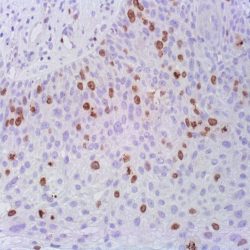
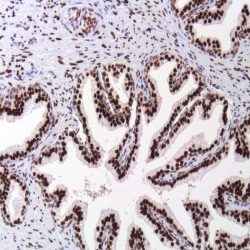
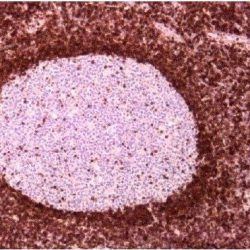
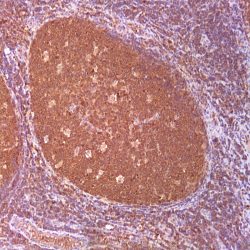
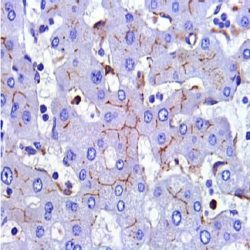
NUT carcinoma (NC, formerly NUT midline carcinoma) is a rare, aggressive subtype of squamous cell carcinoma defined by a chromosomal rearrangement of the NUT gene (also known as NUTM1, nuclear protein in testis). It usually arises in the midline of the body including the thorax, mediastinum, lung (thoracic regions ~50 %) and head and neck area (~40 %), but has also been diagnosed arising outside the midline including salivary gland, pancreas, bladder, kidney, adrenal gland as well as various soft tissue and bone locations. NC is a nearly uniformly lethal cance with a reproducible 6.5 month median overall survival. Although NC can occur at any age, it affects primarily adolescents and young adults with median age of 24. In the majority of cases (~75 %), NUT is fused to BRD4. This results in a chimeric powerful BRD4 NUT oncoprotein. Variant NUT fusion partners, including BRD3, NSD3, ZNF532, and ZNF592, encode BRD4 interacting proteins that serve to link NUT with BRD4. Diagnosis of NC can be established by positive NUT nuclear immunohistochemical staining.