دسته: مونوکلونال
نمایش 461–477 از 477 نتیجه
فیلتر ها-
آنتی بادیهای ایمونوهیستوشیمی
آنتی بادی SOX11 کلون ILQ158 برند Patho Sage
نمره 0 از 5Specification:
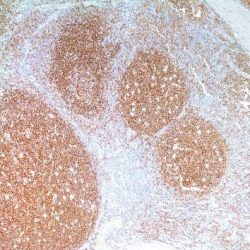
Mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) accounts for 5% to 10% of mature B-cell neoplasms and is an aggressive disease genetically characterized by overexpression of cyclin D1 (CCND1) due to the specific translocation t(11;14) (q13;q32)1. It is necessary that MCL be distinguished from potential morphologic mimics, including chronic lymphocytic leukemia/ small lymphocytic lymphoma (CLL/SLL), follicular lymphoma (FL), and marginal zone lymphoma (MZL) based on immunohistochemical (IHC) staining for CD5, CD23, and CD101. MCL and CLL both express CD5 but MCL, in contrast to CLL, generally lacks CD23 expression by IHC. FL lacks expression of both CD5 and CD23 but most often expresses CD10, whereas MZL is typically negative for all 3 antigens1. Cyclin D1 overexpression is thus the hallmark of MCL even though approximately 5%-10% of MCLs lack Cyclin D1 expression and may be misdiagnosed by overreliance on CyclinD1 IHC2-3. The recognition of cyclin D1negative MCL is difficult because it may resemble other small B-cell lymphomas morphologically and phenotypically4. Although the clinical information on cyclin D1-negative MCL is limited, published data indicate that the behavior of the variant is as aggressive as that of conventional MCL4,5. On the other hand, patients with small B-cell lymphomas mimicking MCL have a significantly better outcome than those with true MCL. It is, therefore, important to find reliable biomarkers that may allow the identification of cyclin D1-negative MCL in clinical practice.
SOX-11, the SRY (sex-determining region Y)-box11 gene, a transcription factor, normally is expressed in the developing human central nervous system6, medulloblastoma7, and glioma8. In a series study4, SOX- 11 expression was investigated in 54 cyclin D1-positive MCL and 209 other lymphoid neoplasms. Interestingly, nearly all MCL were strongly positive for antiSOX-11 (50/54, 93%), with a nuclear pattern. The staining was intense and relatively homogeneous in most of the cells.
Compared to anti-cyclin D1 staining, anti-SOX-11 reactivity was stronger and more homogeneous. Five T-cell and B-cell lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphomas showed strong SOX-11 nuclear expression. One case of classic Hodgkin lymphoma, two of eight BL and two of three T-cell prolymphocytic leukemias were also positive. SOX-11 protein expression was examined by immunohistochemistry in the 12 cyclin D1-negative MCL, and all of them showed strong nuclear positive staining similar to that occurring in conventional cyclin D1-positive MCL4. The expression of SOX-11 in reactive tonsil, lymph node and spleen specimens was studied4. No nuclear expression was observed in any lymphocyte compartment4. Only cytoplasmic staining was seen in cells from reactive germinal centers. Zeng et al.9 has evaluated SOX- 11 expression by immunohistochemistry in 140 cases of mature B-cell neoplasms, including 4 cases of suspected blastoid MCL that lacked cyclin D1 expression and 8 cases of CD5-positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL). Nuclear expression of SOX-11 was found in cyclin D1-positive MCL (30/30, 100%) and in a case of cyclin D1-negative MCL with typical morphology. SOX-11 was expressed in Burkitt lymphoma (1/5, 20%) and lymphoblastic lymphoma (2/3 T-LBLs, 2/2 B-LBLs, overall 4/5, 80%), whereas all cases of DLBCL (including CD5-positive DLBCL) and other small B-cell neoplasms were negative. The 4 suspected cases of blastoid MCL were also anti-SOX-11-positive. These cases had a complex karyotype that included 12p abnormalities.
Therefore, the authors confirmed prior reports that SOX-11 nuclear expression was a specific marker for MCL, including cyclin D1-negative MCL with typical morphology. Their study indicates that SOX-11 IHC is of value in further defining pathologic features of CD5+ DLBCL. Routine use of anti-SOX-11 in cases of suspected CD5+ DLBCL might help identify additional cases of cyclin D1-negative blastoid MCL.
In summary, nuclear protein expression of SOX-11 is highly associated with both cyclin D1-positve and negative MCL. The detection of this transcription factor is a useful biomarker for identifying true cyclin D1- negative MCL. SOX-11 IHC is of value in further defining pathologic features of CD5+ DLBCL. Routine use of anti-SOX-11 in cases of suspected CD5+ DLBCL might help identify additional cases of cyclin D1-negative blastoid MCL. SOX-11 can also be detected in some BL, LBL and TPLL, although the different morphological and phenotypic features of these malignancies allow easy recognition of the cases of cyclin D1-negative MCL.
Presentation:
This antibody is diluted in Tris Buffer, pH 7.3-7.7, with 1% BSA and <0.1% Sodium Azide
-
آنتی بادیهای ایمونوهیستوشیمی
آنتی بادی MITF (Microphthalmia-Associated Transcription Factor) کلون 34CA5 برند Patho Sage
نمره 0 از 5Specification:
Microphthalmia transcription factor (MITF) gene product, a nuclear transcription factor of the basic-helix-loop-helix type, is thought to play a role in the regulation of genes encoding the enzymes necessary for melanogenesis. These include tyrosinase, TRP-1 and TRP-2. MITF is critical for the embryonic development and postnatal viability of melanocytes.
Immunogen:
Prokaryotic recombinant protein corresponding to 111 amino acids of the N-terminal region of the MITF-M molecule
Presentation:
Liquid tissue culture supernatant containing 15mM sodium azide
-
آنتی بادیهای ایمونوهیستوشیمی
آنتی بادی NUT1 کلون C52B1 برند Patho Sage
نمره 0 از 5Specification:
Nuclear protein in testis (NUT) is normally confined to the germ cells of the testis and ovary (1,2). NUT midline carcinoma (NMC) is a recently recognized cancer that is defined by the presence of chromosomal rearrangements involving the NUT gene on chromosome 15q14 (3). In most cases the chromosomal translocation occurs between NUT and BRD4 on chromosome 19, resulting in the formation of a BRD4-NUT fusion protein. In the remaining tumours, variant NUT rearrangements are present involving BRD3, a very close homolog of BRD4. BRD4-NUT and BRD3-NUT encode fusion proteins that appear to contribute to carcinogenesis by blocking epithelial cell differentiation. NMCs, which are aggressive and highly lethal carcinomas, are morphologically indistinguishable from other poorly differentiated carcinomas. Given the limited expression of endogenous NUT protein, this antibody can be used to detect NUT fusion proteins in tissues by immunohistochemistry and immunofluorescence (2). NUT (C52B1) Rabbit mAb detects endogenous levels of total NUT protein. The antibody also detects endogenous levels of the BRD4-NUT fusion protein found in NUT midline carcinoma (NMC).
Immunogen:
Recombinant protein corresponding to the human NUT protein
Presentation:
Supplied in 10 mM HEPES (pH 7.5), 150 mM NaCl, 100 μg/ml BSA, 50% glycerol and less than 0.02% sodium azide
-
آنتی بادیهای ایمونوهیستوشیمی
آنتی بادی CD19 کلون LE-CD19 برند Patho Sage
نمره 0 از 5Specification:
LE-CD 19 recognizes CD19, a 95 kD cell surface glycoprotein, which is expressed by cells of the B cell lineage and follicular dendritic cells. CD 19 is absent on plasma cells. CD 19 is an important signal transduction molecule which is involved in the regulation of B lymphocyte development, activation and differentiation. LE-CD 19 detects a band of approximately 95 kDa in Raji cell lysates under reduction conditions.
Immunogen:
CD19 peptide CGPDPAWGGGGRMGTWSTR (C-terminus) coupled to KLH
Presentation:
purified IgG prepared by affinity chromatography at 200µg/ml in PBS, pH with BSA and Sodium Azide
-
آنتی بادیهای ایمونوهیستوشیمی
آنتی بادی CD38 کلون 38C03 برند Vitro
نمره 0 از 5Name: CD38 Monoclonal Antibody clone 38C03
DESCRIPTION AND APPLICATIONS: CD38 is a single chain type II integral transmembrane protein, which is highly expressed on thymocytes. It is also present on activated T cells and terminally differentiated B cells (plasma cells). Other reactive cells include NK cells, monocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells. CD38 may be detected on cells from multiple myeloma, ALL (B and T) and some AML. It is, however, not found on most mature resting peripheral lymphocytes. CD38 functions as a multicatalytic ectoenzyme serving as ADP-ribosyl cyclase, cyclic ADP-ribose hydrolase and possibly NAD+ glycohydrolase or as a cell surface receptor. Antibodies to CD38 are useful in subtyping of lymphomas and leukemias, detection of plasma cells (i.e. identification of myelomas), and as a marker for activated B and T cells.
COMPOSITION: Anti-human CD38 mouse monoclonal antibody purified from serum and prepared in 10mM PBS, pH 7.4, with 0.2% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide
INTENDED USE: Immunohistochemistry (IHC) on paraffin embedded tissues. Not tested on frozen tissues or Western-Blotting
IMMUNOGEN: Recombinant protein encoding the extracellular domain of human CD38.
SPECIES REACTIVITY: In vitro diagnostics in humans. Not tested in other species
-
آنتی بادیهای ایمونوهیستوشیمی
آنتی بادی CD45 کلون 2B11 & PD7/26 برند Vitro
نمره 0 از 5Name: CD38 Monoclonal Antibody clone 2B11 & PD7/26
DESCRIPTION AND APPLICATIONS: Anti-CD45 (anti leukocyte common antigen) is routinely used to aid the differential diagnosis of undifferentiated neoplasms, whenever malignant lymphoma is suspected by the morphological or clinical data. It is a highly specific antibody; therefore a positive result is highly indicative of hematolymphoid origin. Certain types of hematolymphoid neoplasms may lack CD45(Hodgkin lymphoma, some T-cell lymphomas, and some leukemias) so its absence does not rule out a hematolymphoid tumor. This antibody is expressed almost exclusively by cells of hematopoietic lineage and is present in most benign and malignant lymphocytes as well as plasma cell precursors.
COMPOSITION: Anti-human CD45, also known as leukocyte common antigen, is a mouse monoclonal antibody purified from serum and prepared in 10mM PBS, pH 7.4, with 0.2% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide
INTENDED USE: Immunohistochemistry (IHC) on paraffin embedded tissues. Not tested on frozen tissues or Western-Blotting
SPECIES REACTIVITY: In vitro diagnostics in humans. Not tested in other species
-
آنتی بادیهای ایمونوهیستوشیمی
آنتی بادی CD42b کلون EPR19204 برند Vitro
نمره 0 از 5Name: CD42b Monoclonal Antibody clone EPR19204
DESCRIPTION AND APPLICATIONS: The CD42b glycoprotein, also known as GPIb, is a co-factor of ristocetin-induced aggregation and is involved in the binding of platelets to blood vessel walls. The CD42b antigen is expressed on platelets and on megakaryocytes in bone marrow. The absence of CD42b antigen on platelets may indicate Bernard Soulier disease. The antibody is of value in theimmunophenotyping of megakaryoblastic leukaemias that express one or more markers associated with platelets (CD41, CD61 and CD42b). In chronic myeloproliferative processes, like chronic idiopathic myelofibrosis in prefibrotic stage besides appearing in greater numbers the megakaryocytes are markedly abnormal while megakaryocytes in unclassifiable myelodysplastic / myeloproliferative diseases there is an increased of normal or small megakaryocytes (micromegakaryocytes).
COMPOSITION: Anti-human CD42b rabbit monoclonal antibody purified from hybridoma and, diluted in a pH7.6 buffer containing stabilizing protein and sodium azide as bacteriostatic and bactericidal agent.
INTENDED USE: Immunohistochemistry (IHC) on paraffin embedded tissues. Not tested on frozen tissues or Western-Blotting
IMMUNOGEN: Recombinant CD42b.
SPECIES REACTIVITY: In vitro diagnostics in humans. Not tested in other species
-
آنتی بادیهای ایمونوهیستوشیمی
آنتی بادی Cdk4 کلون CDK4/7987R برند Vitro
نمره 0 از 5Name: Cdk4 Monoclonal Antibody clone CDK4/7987R
DESCRIPTION AND APPLICATIONS: Cell cycle progression is controlled in part by a family of cyclin proteins and cyclin dependent kinases (Cdks). Cdk proteins work in concert with the cyclins to phosphorylate key substrates involved in each phase of cell cycle progression. Another family of proteins, Cdk inhibitors, also plays a role in regulating the cell cycle by binding to cyclin Cdk complexes and modulating their activity. Several Cdk proteins have been identified, including Cdk2 Cdk8, PCTAIRE-1-PCTAIRE-3, PITALRE and PITSLRE. Cdk4, in complex with D-type cyclins, is thought to regulate cell growth during the G1 phase of the cell cycle. This association with a D-type cyclin upregulates Cdk4 activity, whereas binding to the Cdk inhibitor p16 downregulates Cdk4 activity. Activation of the Cdk4-cyclin complexes requires phosphorylation on a single threonyl residue of Cdk4, catalyzed by a Cdk-activating protein (CAK).
COMPOSITION: Anti-human CDK4 rabbit monoclonal antibody diluted in a pH 7.6 buffer containing stabilizing protein and sodium azide as bacteriostatic and bactericidal agent.
INTENDED USE: Immunohistochemistry (IHC) on paraffin embedded tissues. Not tested on frozen tissues or Western-Blotting
IMMUNOGEN: Recombinant fragment corresponding to N-terminal of human CDK4 protein
SPECIES REACTIVITY: In vitro diagnostics in humans. Not tested in other species
-
آنتی بادیهای ایمونوهیستوشیمی
آنتی بادی WT1 (Wilms Tumor) کلون 6F-H2 برند PathoSage
نمره 0 از 5Intended use:
This antibody is intended for in vitro diagnostic (IVD) use. Primary Antibody is intended for professional laboratory use in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded (FFPE) tissue stained in manual qualitative immunohistochemistry (IHC) testing. A qualified pathologist must interpret the results using this product to aid diagnosis in conjunction with the patient’s relevant clinical history, other diagnostic tests, and proper controls.
Presentation:
supernatant prepared in 10mM PBS, pH 7.4, with %0.2 BSA and %0.09 sodium azide Anti-human WT-1 mouse monoclonal antibody obtained from tissue culture
-
آنتی بادیهای ایمونوهیستوشیمی
آنتی بادی VIP کلون H-6 برند PathoSage
نمره 0 از 5Intended use:
This antibody is intended for in vitro diagnostic (IVD) use. Primary Antibody is intended for professional laboratory use in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded (FFPE) tissue stained in manual qualitative immunohistochemistry (IHC) testing. A qualified pathologist must interpret the results using this product to aid diagnosis in conjunction with the patient’s relevant clinical history, other diagnostic tests, and proper controls.
Presentation:
Anti-human VIP mouse monoclonal antibody purified from serum and prepared in PBS with < %0.1 sodium azide and %0.1 gelatin
-
آنتی بادیهای ایمونوهیستوشیمی
آنتی بادی Vimentin کلون SP20 برند PathoSage
نمره 0 از 5Intended use:
This antibody is intended for in vitro diagnostic (IVD) use. Primary Antibody is intended for professional laboratory use in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded (FFPE) tissue stained in manual qualitative immunohistochemistry (IHC) testing. A qualified pathologist must interpret the results using this product to aid diagnosis in conjunction with the patient’s relevant clinical history, other diagnostic tests and proper controls.
Presentation:
Anti-human Vimentin rabbit monoclonal antibody purified from serum and prepare din 10mM PBS, pH 7.4, with %0.2 BSA and %0.09 sodium azide
-
آنتی بادیهای ایمونوهیستوشیمی
آنتی بادی Villin 1 کلون CWWB1 برند PathoSage
نمره 0 از 5Intended use:
This antibody is intended for in vitro diagnostic (IVD) use. Primary Antibody is intended for professional laboratory use in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded (FFPE) tissue stained in manual qualitative immunohistochemistry (IHC) testing. A qualified pathologist must interpret the results using this product to aid diagnosis in conjunction with the patient’s relevant clinical history, other diagnostic tests, and proper controls.
Presentation:
Anti-human Villin-1 mouse monoclonal antibody purified from serum and prepared in 10mM PBS, pH 7.4, with %0.2 BSA and %0.09 sodium azide
-
آنتی بادیهای ایمونوهیستوشیمی
آنتی بادی VEGF (Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor) کلون EP1176Y برند PathoSage
نمره 0 از 5Intended use:
This antibody is intended for in vitro diagnostic (IVD) use. Primary Antibody is intended for professional laboratory use in formalin fixed, paraffin-embedded (FFPE) tissue stained in manual qualitative immunohistochemistry (IHC) testing. A qualified pathologist must interpret the results using this product to aid diagnosis in conjunction with the patient’s relevant clinical history, other diagnostic tests, and proper controls.
Presentation:
Anti-human VEGF Rabbit monoclonal antibody purified from ascites fluid by Protein A chromatography prepared in 10mM PBS, pH 7.4, with %0.2 BSA and %0.09 sodium azide
-
آنتی بادیهای ایمونوهیستوشیمی
آنتی بادی Uroplakin 3 کلون BC17 برند PathoSage
نمره 0 از 5Intended use:
This antibody is intended for in vitro diagnostic (IVD) use. Primary Antibody is intended for professional laboratory use in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded (FFPE) tissue stained in manual qualitative immunohistochemistry (IHC) testing. A qualified pathologist must interpret the results using this product to aid diagnosis in conjunction with the patient’s relevant clinical history, other diagnostic tests, and proper controls.
Presentation:
Anti-human Uroplakin III mouse monoclonal antibody purified from serum and prepared in 10mM PBS, pH 7.4, with %0.2 BSA and %0.09 sodium azide
-
آنتی بادیهای ایمونوهیستوشیمی
آنتی بادی Uroplakin 2 کلون BC21 برند PathoSage
نمره 0 از 5Intended use:
This antibody is intended for in vitro diagnostic (IVD) use. Primary Antibody is intended for professional laboratory use in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded (FFPE) tissue stained in manual qualitative immunohistochemistry (IHC) testing. A qualified pathologist must interpret the results using this product to aid diagnosis in conjunction with the patient’s relevant clinical history, other diagnostic tests, and proper controls.
Presentation:
Anti-Uroplakin 3 mouse monoclonal antibody obtained from supernatant culture and prediluted in a tris buffered solution pH 7.4 containing 0.375mM sodium azide solution as bacteriostatic and bactericidal
-
آنتی بادیهای ایمونوهیستوشیمی
آنتی بادی TSH (Thyroid Stimulating Hormone) کلون EP254 برند PathoSage
نمره 0 از 5Intended use:
This antibody is intended for in vitro diagnostic (IVD) use. Primary Antibody is intended for professional laboratory use in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded (FFPE) tissue stained in manual qualitative immunohistochemistry (IHC) testing. A qualified pathologist must interpret the results using this product to aid diagnosis in conjunction with the patient’s relevant clinical history, other diagnostic tests, and proper controls.
Presentation:
Anti-human TSH (Thyroid Stimulating Hormone) rabbit monoclonal antibody purified from serum and prepared in 10mM PBS, pH 7.4, with %0.2 BSA and %0.09 sodium azide
-
آنتی بادیهای ایمونوهیستوشیمی
آنتی بادی Estrogen Receptor کلون MXR030 برند PathoSage
نمره 0 از 5Intended Used: This antibody is intended for research use only (RUO). It is designed for professional laboratory use in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded (FFPE) tissue stained in manual qualitative immunohistochemistry (IHC) testing. In addition to FFPE tissues, this antibody may be tested on frozen tissues or applied in Western blot analyses.
Presentation: Rabbit monoclonal Antibody. Tissue culture supernatant with %0.2 BSA and 15mM sodium azide