Name: CD25 antibody clone 4C9
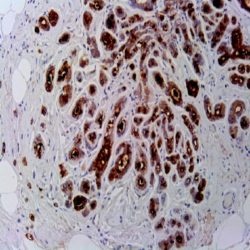
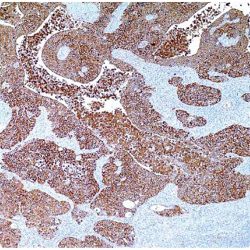
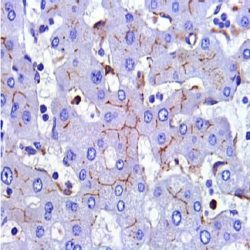
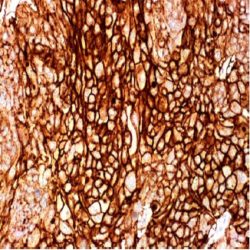
Description and aplications: The CD25 molecule, also known as IK-2 receptor alpha, IL2RA, p55, T-cell growth factor receptor (TCGFR) or TAC antigen is an activation antigen present, along with CD4, in regulatory T cells. The gene that controls its expression, with 8 exons and over 25 kb, codes the alpha subunit of the cell surface receptor IL-2 and is located in the chromosome region 10p15.1. The regulatory T cells, since they suppress the activation of autoreactive T cells controlling the immune tolerance, prevent autoimmune diseases and, as negative collateral effects, avoid the destruction of tumor cells by cytotoxic T lymphocytes and act as suppressors of the NK cells. Partial deletions of the CD25 gene are responsible for immunodeficiency 41 (characterized by the association of various lymphoproliferative syndromes with autoimmune diseases) and insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus type 10, a variant of diabetes mellitus type I associated with autoimmune diseases and with typical familial aggregation. In normal tissues, CD25 can be expressed by activated B and T lymphocytes, macrophages and osteoblasts. Some thymocytes, myeloid precursors and oligodendrocytes can also show immunostaining. This molecule is not expressed in normal mastocytes. According to the classification system of the World Health Organization, the main diagnostic criterion for the involvement of bone marrow by systemic mastocytosis (SM) is the presence of dense aggregates (more than 15 cells) of mastocytes. For this reason, the aberrant expression of CD25 as a low affinity receptor for interleukin-2 (IL-2) by neoplastic mast cells is a good diagnostic tool to distinguish them from reactive proliferations of mast cells, and for this reason it has recently become a minor criterion for the diagnosis of SM, where aberrant staining of mastocytes aggregates by anti-CD25 antibody is diagnostic of SM. The anti-CD25 antibody has also been useful for the identification of mastocytes on skin biopsies in the context of urticaria pigmentosa as a predictor of systemic mastocytosis. Additionally, the quantification of regulatory T-cells (Treg) expressing CD25 in the context of hepatocellular carcinoma has been used as an independent predictor of tumor recurrence following liver resection of a previous hepatocellular carcinoma. In addition, the percentage of regulatory T cells FOXP3+ CD25+ infiltrating between melanoma tumor cells and in their periphery is significantly higher in melanomas with recurrent capacity than in their non-recurrent forms.
Finally, CD25 together with CD103 and CD123 is useful for completing the panel of markers of hairy cell leukemia, although the latter two antibodies have greater specificity and sensitivity for this diagnosis than CD25 itself.
Similarly, due to its general low specificity, the CD25 antibody’s positive staining should be evaluated within an antibody panel, not in isolation, and in correlation with the remaining morphological aspects of the lesions analyzed since many B lymphomas, T lymphomas, or even anaplastic large cell lymphoma may present staining against this marker.
Composition: anti-CD25 mouse monoclonal antibody obtained from supernatant culture and prediluted in a tris buffered solution pH 7.4 containing 0.375mM sodium azide solution as bacteriostatic and bactericidal.
Intended use: Immunohistochemistry (IHC) on paraffin embedded tissues. Not tested on frozen tissues or Western-Blotting
Immunogen: Recombinant protein corresponding to the external domain of the human IL-2R


دیدگاهها
هیچ دیدگاهی برای این محصول نوشته نشده است.