Category: monoclonal
Showing 61–80 of 412 results
فیلتر ها-
آنتی بادیهای ایمونوهیستوشیمی
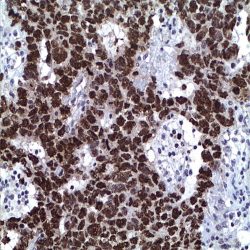
آنتی بادی TRAF1 (TNF receptor-associated factor 1) (H3)
Rated 0 out of 5.(Name: TRAF1 (TNF receptor-associated factor 1) Antibody (clone H3
Description and applications: This antibody recognises TRAF1, with a molecular mass of 52 kDa, codified by TRAF1 gene, located in chromosome 9q33.2. TRAF (TNF receptor-associated factor) constitutes a family of adapter proteins (TRAFs 1-6) that bind to different membrane receptors to initiate different signalling pathways related to cell death and survival through the activation of NF-κB and pro-mitogenic protein kinases. Tumour necrosis factor (TNF) activates different cellular signals through TNF-R1 and TNF-R2 receptors, belonging to the TNF receptor superfamily, which includes CD95 or FAS and CD40. TRAF1 and TRAF2 are TNF receptor-associated factor 1 and 2, respectively. Together, they form a heterodymeric complex associated with TNF-R2’sintracytoplasmic domain. A third member of the family, or TRAF-3 (also known as CD40bp, CRAF-1 or LAP1), has been identified; it associates with the intracytoplasmic domain of CD40. TRAF is the major signal transducer for TNF and IL- 1/TLR receptor superfamilies, playing an important role in innate and adaptive immunity. TRAF1 is expressed in cells latently infected with Epstein-Barr virus. It may be a useful indicator in EBVassociated nasopharyngeal carcinomas by predicting the induction of apoptosis secondary to chemotherapy.
Composition:Anti-human TRAF1 (TNF receptor-associated factor 1) mouse monoclonal antibody purified from serum and prepared in 10mM PBS, pH 7.4, with 0.2% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide.
Immunogen:Synthetic peptide corresponding to aa 173-295 of the central region of human TRAF-1.
-
آنتی بادیهای ایمونوهیستوشیمی
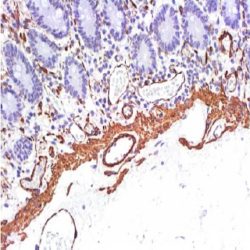
آنتی بادی Tartrate Resistant Acid Phosphatase (9C5)
Rated 0 out of 5Name: Mouse anti-human Tartrate-Resistant Acid Phosphatase (TRAcP) Monoclonal Antibody (Clone 9C5)
Description and applications: Tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAcP) is a basic iron-binding protein with high activity towards phosphoproteins, ATP and 4-nitrophenyl phosphatase. It is detected in human alveolar macrophages, osteoclasts, spleen and liver. Its expression is increased in spleen and monocytes of patients with Gaucher’s disease; spleen of patients with Hodgkin’s lymphoma and in the sera of patients undergoing active bone turnover.
The histochemical identification of hairy cell leukemia via tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase assay has been a standard for over two decades. Anti-TRAcP antibody labels the cells of hairy cell leukemia (HCL) with a high degree of sensitivity and specificity.Composition: anti-human TRAcP mouse monoclonal antibody purified from serum and prepared in 10mM PBS, pH 7.4, with 0.2% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide.
-
آنتی بادیهای ایمونوهیستوشیمی
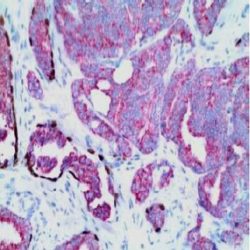
آنتی بادیtotal PSA-کلون HS-5
Rated 0 out of 5Name: total PSA Antibody (Clone HS-5)
Description and applications: PSA is an antigen present in prostatic tissue and in the majority of prostatic carcinomas. This antibody recognizes primary and metastatic prostatic neoplasms and rarely in tumors of nonprostatic origin. These include breast and a minority of salivary gland tumors. The antigen is a 33-34 kD glycoprotein that is restricted to epithelial cells of the prostate.
Because of the high specificity of PSA for prostate glandular epithelium, the antibody is useful to identify prostatic carcinomas of the prostate and their frequent infiltration of the surrounding organs (eg .: rectum and urinary bladder). Rectal adenocarcinomas, urothelial carcinoma or adenocarcinoma of the urinary bladder did not express PSA. The loss of immunoreactivity for PSA which can occur in poorly differentiated neoplasms cannot completely exclude the diagnosis of prostate cancer with a negative PSA. Another important use is for differential diagnosis and determine the origin of the primary tumor with metastases of unknown origin, especially lymph node and bone. PSA can be used together with the Prostein, which has at least the same sensitivity and is slightly more specific than PSA.Composition: anti-human total PSA mouse monoclonal antibody purified from hybridoma cell culture by hydrophobic interaction chromatography using ammonium sulphate. Prepared in 10mM PBS, pH 7.4, with 0.2% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide.
-
آنتی بادیهای ایمونوهیستوشیمی
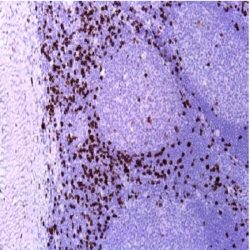
آنتی بادی TLE1 (1F5)
Rated 0 out of 5Name: TLE-1 Antibody (Clone 1F5).
Description and aplications: Transducin-like enhancer of split 1 (TLE1) gene is a member of the TLE gene family and involved in control of hematopoiesis, neuronal, and terminal epithelial differentiation. By immunohistochemistry in formalin-fixed, paraffinembedded tissues, TLE1 expression (nuclear staining) has been found in 249 of 259 molecularly confirmed synovial sarcoma cases, and was rare to absent in the 73 other soft tissue tumors examined (positive staining was found only in 1 of 43 malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors and 1 pleomorphic sarcoma). Anti-TLE1 was more sensitive and specific for synovial sarcoma than other currently available immunohistochemical markers including BCL2, epithelial membrane antigen and cytokeratins, and had a positive predictive value of 92% and a negative predictive value of 100% in this clinical setting. TLE1 overexpression is significantly associated with the t(X;18) translocation.
Composition: anti-human TLE-1 mouse monoclonal antibody purified from ascites fluid by chromatography. Prepared in 10mM PBS, pH 7.4, with 0.2% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide.
-
آنتی بادیهای ایمونوهیستوشیمی
آنتی بادی TIA1 (2G9A10F5)
Rated 0 out of 5Name: TiA1 Antibody (Clone 2G9A10F5)
Description and aplications: The T cell intracellular antigen 1 (TIA-1) is a 17-kDa cytoplasmic granule associated protein also designated as GMP-17, for granule membrane protein of 17 kDa. The GMP-17/TIA-1 molecule is expressed in cells possessing cytolytic potential and could be involved in the signalling cascade of Fas (CD95)-mediated apoptosis.
Within hematopoietic cell lines, the 2G9 monoclonal antibody (mAb) reacts with about 90% of CD16+, 50 – 60% of CD8+, and less than 10% of CD4+ normal peripheral blood lymphocytes. It reacts with almost all monocytes
and granulocytes. This antibody also reacts with CD4+ activated T-cell clones, activated NK cell clones, and Con-A activated thymocytes, but not with B lymphocytes or B-cell lines.Composition: anti-human TiA1 mouse monoclonal antibody purified from ascites fluid by affinity chromatography. Prepared in 10mM PBS, pH 7.4, with 0.2% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide.
Immunogen: Human bone marrow malignant cells from a non-B, non-T acute leukemia.
-
آنتی بادیهای ایمونوهیستوشیمی
آنتی بادی Thyroid Peroxidase (EP159)
Rated 0 out of 5Name: Thyroid Peroxidase Antibody (Clone EP159)
Description and applications:Thyroid peroxidase (TPO) is a type I glycosylated protein located in the apical membrane of thyroid follicular cells. Its secretion is controlled by the TPO gene, located in the chromosomal region 2p25.3. Under normal conditions, it plays an important role in the synthesis of thyroid hormones by catalysing iodine oxidation and binding to tyrosine residues to form iodotyrosine. It also regulates the binding of iodotyrosine residues for the formation of active hormonal elements such as thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). Mutations in the TPO gene are responsible for type 2A thyroid dysmorphogenesis (TDH2A), manifested primarily with congenital hypothyroidism. According to studies of its mRNA, the expression of TPO isreduced in thyroid carcinomas and has normal levels in non-secreting adenomas (cold). Likewise, high levels of TPO have been detected in toxic adenomas and in Graves’ disease. As TPO reflects the thyroid gland normal function and, therefore, it should not be expressed in malignant lesions, its presence in the cytoplasm of tumour thyreocytes has been explored in the difficult differential diagnosis between follicular and papillary thyroid carcinomas. Depending on the series of studies considered, TPO functions as a negative marker for the diagnosis of malignant thyroid lesions, with a variable sensitivity between 44% and 100% and a specificity ranging from 68% to 100%. Likewise, loss of TPO expression is more specific for papillary carcinomas than for follicular carcinomas, although expression loss in malignant lesions is variable and there is no generally accepted consensus regarding the percentage of negative cells needed to support the diagnosis of malignancy. For this reason, TPO expression should always be assessed in conjunction with other markers and be supported by the morphological changes observed in the lesion. Studies in the literature indicate that anti-TPO, together with antibodies against HBME-1, galectin-3, and cytokeratin 19, may be included in an immunohistochemical marker panel for the identification of papillary thyroid carcinoma and some of the follicular variants of this neoplasm. Finally, the sustained expression of TPO in morphologically malignant lesions has been considered as a possible positive prognostic factor since it suggests conserved thyroid function.
Composition: Anti-human Thyroid Peroxidase rabbit monoclonal antibody purified from serum and prepared in 10mM PBS, pH 7.4, with 0.2% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide.
Immunogen: Synthetic peptide corresponding to Cterminal residues from human protein TPO.
-
آنتی بادیهای ایمونوهیستوشیمی
آنتی بادی Thyroglobulin (EP250)
Rated 0 out of 5Name: Thyroglobulin Antibody (Clone EP250)
Description and applications: Thyroglobulin (TG) is a dimeric glycoprotein specific to the thyroid gland which belongs to the type-B carboxylesterase/lipase family. It is the precursor of the iodinated thyroid hormones triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4). Variations in TG are associated with susceptibility to autoimmune thyroid disease type 3, and defective or impaired TG synthesis usually results in congenital goitrous hypothyroidism, virtual absence of TG in thyroid tissue, and the presence of an elevated concentration of iodoalbumin. The final result of these abnormalities is a decreased rate of T3 and T4 synthesis.
Thyroglobulin is found in normal thyroid and differentiated thyroid carcinoma cells but not undifferentiated thyroid. Thyroglobulin is a useful marker for identification of tumors with thyroid origin.Composition: anti-human Thyroglobulin rabbit monoclonal antibody purified from ascites. Prepared in 10mM PBS, pH 7.4, with 0.2% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide.
Immunogen: A synthetic peptide corresponding to residues of human Thyroglobulin protein.
-
آنتی بادیهای ایمونوهیستوشیمی
آنتی بادی Thrombomodulin (EP175)
Rated 0 out of 5Name: Thrombomodulin Antibody (Clone EP175)
Description and applications: Thrombomodulin (TM) is a transmembrane glycoprotein of 75 kDa molecular mass with six repeated domains homologous to the epidermal growth factor and a terminal domain homologous to the lectin-like proteins. Thrombomodulin actives anticoagulant proteins derived from vitamin K synthesized in the liver (proteins C and S) which bind to thrombin in order to prevent thrombus formation in the endothelial surface of the vessel. TM expression is upregulated by agents that increase cAMP and down through the interleukin I, tumor necrosis factor (TNF) and some endotoxins. The TM 1009, bindsto domains 4 and 6 of the epidermal growth factor, the smallest region which binds to thrombin. This binding may interfere with the binding between thrombin and thrombomodulin. This antibody produced immunostaining in a variety of normal cells: endothelial lining blood vessels and lymphatics cells, mesothelial cells, normal urothelium, some pulmonary alveolar macrophages, coating meningeal cells, synoviocytes, syncytiotrophoblasts, megakaryocytes and platelets. Thrombomodulin is also found in some subtype cell of pancreatic islets and in peripheral nerves. It is diagnostically useful in neoplastic cells of vascular tumors, urothelial carcinomas, meningiomas, adenomatoid tumor, choriocarcinoma and pleural tumors. TM can be used for differential diagnosis between mesothelioma (positive) and lung adenocarcinoma (consistently negative). Weak expression of TM was demonstrated in two thirds of the cases examined, while a strong TM staining was revealed in one third of colon cancers.
Composition: anti-Thrombomodulin rabbit monoclonal antibody obtained from supernatant culture and prediluted in a tris buffered solution pH 7.4 containing
0.375mM sodium azide solution as bacteriostatic and bactericidal.Immunogen: A synthetic peptide corresponding to residues at the C-terminus of human thrombomodulin protein.
-
آنتی بادیهای ایمونوهیستوشیمی
آنتی بادی Transcription Factor E3 (TFE3) (MD-37, also known as MRQ-37)
Rated 0 out of 5Name: Transcription Factor E3 (TFE3) Antibody(Clone MD-37 )
Description and applications:Xp11 translocation renal cell carcinomas (RCC) are a recently recognized subset of RCC, characterized by chromosome translocations involving the Xp11.2 break point and resulting in gene fusions involving the TFE3 transcription factor gene that maps to this locus. Xp11 translocation RCC represents the most common type of RCC in children, but is less frequent on a percentage basis in adults. Morphologically, these neoplasms frequently show papillary architecture and clear cytoplasm, and frequently have associated psammoma bodies. Immunohistochemically, these neoplasms under-expresses epithelial markers such as anti-cytokeratin and anti-epithelial membrane antigen (anti-EMA) compared with typical adult type RCC. Themost sensitive and specific immunohistochemical marker for the Xp11 translocation RCC is nuclear labeling of TFE3 protein, which reflects overexpression of the resulting fusion proteins relative to native TFE3. Alveolar soft part sarcoma (ASPS) is an uncommon soft tissue sarcoma of undertain differentiation. It presents in younger patients, often in the extremities. Despite relatively high rates of metastasis, patients often experience prolonged survival in the metastatic setting relative to others. The hallmark of ASPS is a chromosomal rearrangement at 17q25 and Xp11.2 engendering an ASPSCR1-TFE3 fusion gene responsible for an aberrant transcription factor presumably enabling pathogenesis. This aberrant chimeric transcription factor retains the N-terminal DNA binding domain encoded by TFE3 while the ASPSCR1 encoded portion probably provides domain(s) modulating gene expression. The presence of this ‘super-activated’ transcription factor may induce the expression of numerous molecules contributing to ASPS diagnosis, progression, and metastasis. Even if highly sensitive for Xp11 translocation renal cell carcinomas diagnosis, clear cell carcinomas, especially cells surrounding areas of necrosis, might also be positive. For these reason is recommended to confirm the diagnostic using FISH specific probes.
Composition: Anti-human TFE3 rabbit monoclonal antibody purified from serum and prepared in 10mM PBS, pH 7.4, with 0.2% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide.
-
آنتی بادیهای ایمونوهیستوشیمی
آنتی بادی TdT (EP266)
Rated 0 out of 5Name: TdT Antibody (Clone EP266)
Description and aplications:Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT) is a unique DNA polymerase that changes the addition of deoxynucleoside 5’- triphosphate to the 3’-end of a DNA initiator without template direction. TdT contributes to the generation of junctional diversity in antigen receptors of immature lymphocytes.
TdT is expressed in lymphoid precursors of B- and T-cell lineage in thymus and bone marrow. Foci of TdT positive cells may be observed in peripheral lymphoid tissues. TdT is also present in malignant tumors of lymphoblastic lineage and thymoma. It is a sensitive and specific marker for lymphoblastic lymphoma/leukemia.Composition: anti-human Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT) Rabbit monoclonal antibody prepared in 10mM PBS, pH 7.4, with 0.2% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide.
Immunogen: A synthetic peptide corresponding to residues of human TdT protein.
-
آنتی بادیهای ایمونوهیستوشیمی
آنتی بادی TCR C Gamma M1 (H-41)
Rated 0 out of 5Name: TCR gamma M1 Antibody Clone H-41
Description and applications: The antibody detects TCR C gamma M1 which has a predicted molecular
weight of approximately 18 kDa.
The ability of T cell receptors (TCR) to discriminate foreign from self-peptides presented by major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II molecules is essential for an effective adaptive immune response. TCR recognition of self-peptides has been linked to autoimmune disease. Mutant self-peptides have been associated with tumors. Engagement of TCRs by a family of bacterial toxins know as superantigens has been responsible for toxic shock syndrome. Autoantibodies to V beta segments of T cell receptors have been isolated from patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). The autoantibodies block TH1-mediated inflammatory autodestructive reactions and are believed to be amethod by which the immune system compensates for disease.
T Cell and TCR Diversity Most human T cells express the TCR alpha-beta and either CD4 or CD8 molecule (single positive, SP). A small number of T cells lack both CD4 and CD8 (double negative, DN). Increased percentages of alpha-beta DN T cells have been identified in some autoimmune and immunodeficiency disorders. Gamma-delta T cells are primarily found within the epithelium. They show less TCR diversity and recognize antigens differently than alpha-beta T cells. Subsets of gamma-delta T cells have shown antitumor and immunoregulatory activity.
The antibody has a particular utility in the diagnostic of the four major subtypes of predominantly γδ T-cell lymphomas that are currently recognized: 1) hepatosplenic γδ T lymphoma; 2) Subcutaneous panniculitis-like T cell lymphoma; 3) primary cutaneous γδ T cell lymphoma and 4) IInd subtype of lymphoma associated with enteropathy. However, the antibody against the gamma chain of the TCR molecule can be positive in isolated case of mycosis fungoides or lymphomatoid papulosis. Consequently, the clinical and histological context in which the lesion occurs together with other immunocytochemical markers, must be taken into account when specifying the diagnosis.Composition: anti-human TCRgamma mouse monoclonal antibody purified from serum and prepared in 10mM PBS, pH 7.4, with 0.2% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide
Immunogen: Human TCR gamma chain constant region.
-
آنتی بادیهای ایمونوهیستوشیمی
آنتی بادی TCL1 (EP105)
Rated 0 out of 5Name: TCL1 Antibody (Clone EP105)
Description and applications:T-cell leukemia/lymphoma protein 1A (TCL1) is a member of the TCL1 family and enhances the phosphorylation and activation of AKT1, AKT2 and AKT3. TCL1 promotes the nuclear translocation of AKT1 and enhances cell proliferation, stabilizes mitochondrial membrane potential and promotes cell
survival. The expression of TCL1 is restricted to lymphoid cells. It is expressed early in lymphocyte differentiation. Strong expression of TCL1 is fouma, follicular lymphoma, Burkitt lymphoma,diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (60%), and primary cutaneous B-cell lymphoma (55%). The expression of the TCL1 gene charactend in a subset of mantle zone B lymphocytes and is expressed to a lesser extent by follicle center cells. In B-cell neoplasia, TCL1 immunoreactivity is found in the majority of B-cell lymphomas including lymphoblastic lymphoma, chronic lymphocytic leukemia, mantle cell lymphorizes low-grade B-cell lymphomas.Composition:Anti-human TCL1 rabbit monoclonal antibody purified from serum and prepared in 10mM PBS, pH 7.4, with 0.2% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide.
Immunogen:Synthetic peptide corresponding to residues in human TCL1 protein.
-
آنتی بادیهای ایمونوهیستوشیمی
آنتی بادی T-Box TBX21 (4B10)
Rated 0 out of 5Name: T-Box/TBX21 Antibody (Clone 4B10)
Description and applications: The T-bet transcription factor (more correctly called T-box TBX21 transcription factor), expressed in T cells, is one of the members of the T-box transcription factor family specific to Th1 cells. It is encoded by a gene located in the chromosomal region 17q21.32. The T-bet factor was originally isolated from nuclear extracts of resting and PMA/ionomycin-activated AE7 lymphoid cells; it is expressed in low levels in resting cells, and in increased levels in stimulated cells. T-bet regulates the secretion of IFN-γ by CD4 Th1 cells (although this mediator is also produced by NK cells and CD8+ cytotoxic T cells, in the latter case, independently of the presence of T-bet). Similarly, and under the right conditions, T-bet also converts effector Th2 cells into the opposing Th1 subset. In mice carrying T-bet gene deletions, lymphocytes differentiate into a predetermined stage of Th2 cells and are protected against lesions equivalent torheumatoid arthritis, which highlights the crucial role that this transcription factor plays in the induction of a Th1 response. For this reason, it is now known that an adequate level of T-bet activation contributes to a decrease of the excessive Th2 response found in bronchial hyperreactivity, oedema, and eosinophil granulocyte infiltration underlying bronchial asthma. In normal tissue, T-bet is expressed selectively and more intensely in Th1 cells, although at a lower level it is also found in NK cells and CD8+ cytotoxic T cells, and its expression level is increased in response to signals mediated by the T cell-specific receptor (TCR) and IL-12. In pathological situations, T-bet, in addition to being involved in the pathogenic mechanisms of some T cell lymphoproliferative processes, also regulates the response in some autoimmune diseases such as Crohn’s disease and type I diabetes mellitus. Finally, the presence of genetic variations in T-bet is associated with a greater susceptibility to bronchial asthma with sinonasal polyposis development and intolerance to aspirin. The implication of T-bet in the pathological development of B cells, as well as the development of some of the neoplastic lesions that are derived from them, has not yet been sufficiently analysed. In neoplasms, the T-bet transcription factor is expressed in all lymphomas originating from mature T cells, especially in peripheral T lymphomas, and is consistently negative in lymphomas derived from T cell precursors (lymphoblastic lymphomas). Likewise, most nasal NK/T lymphomas express nuclear T-bet regardless of the presence of Epstein-Barr virus or the presence of TCR receptor clonal rearrangement. Among B cell-derived neoplasms that most frequently express T-bet are marginal zone lymphomas, both extranodal and splenic, B lymphoblastic leukaemia, and hairy-cell leukaemia, in which T-bet positivity, along with TRAP, DBA.44, CD123, and Annexin-1 positivity, confirm diagnosis. Moreover, this antibody against T-bet has the advantage of being one of the few antibodies that work consistently in spine biopsies with hairy-cell leukaemia infiltration. Other lymphoproliferative lesions that may occasionally express T-bet are B cell chronic lymphocytic leukaemia, diffuse large B cell lymphoma, and classical Hodgkin lymphoma. Likewise, positivity has been described in some adenocarcinomas. In the differential diagnosis between lymphocytic colitis and coeliac disease, predominance of T-betpositive T cells, both in the epithelium and in the lamina propria, supports the latter diagnosis, while positive cells for both T-bet and GATA3 are more characteristic of lymphocytic colitis.
Composition: Anti-human T-Box TBX21 mouse monoclonal antibody purified from serum and prepared in 10mM PBS, pH 7.4, with 0.2% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide.
Immunogen:Recombinant mouse T-bet protein.
-
آنتی بادیهای ایمونوهیستوشیمی
آنتی بادی Synaptophysin (EP158)
Rated 0 out of 5Name:Synaptophysin Antibody (Clone EP158)
Description and applications: Synaptophysin is a major integral transmembrane glycoprotein of synaptic vesicles with four transmembrane domains. This protein is present in almost all neurons and neuroendocrine cells throughout the body. An antibody to Synaptophysin is useful for the identification of tumors with neural and
neuroendocrine differentiation. In well-differentiated tumors containing neurons (gangliocytoma, ganglioglioma, neurocytoma, ganglioneuroblastoma) synaptophysin is consistently expressed. Primitive neuroectodermal tumors (PNET) (cerebral PNET, medulloblastoma, neuroblastoma) show less intensity and variable reactivity.Composition: anti-human Synaptophysin rabbit monoclonal antibody purified from serum and prepared in 10mM PBS, pH 7.4, with 0.2% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide.
Immunogen: A synthetic peptide corresponding to residues on the C-terminus (cytoplasmic domain) of human Synaptophysin protein.
-
آنتی بادیهای ایمونوهیستوشیمی
آنتی بادی SV-40 Virus (PAb416)
Rated 0 out of 5Name: SV40 Antibody (Clone PAb416).
Description and aplications: SV40, Simian Virus 40 is a polyomavirus that is found in both monkeys and humans. Like other polyomaviruses, SV40 is a DNA virus that has the potential to cause tumors. SV40 is believed to suppress the transcriptional properties of tumor-suppressing p53 in humans through the SV40 large T-antigen and SV40 small T-antigen. It is generally assumed that large T-antigen is the major protein involved in neoplastic processes and the large T-antigen predominantly exerts its effect through deregulation of tumor suppressor p53, which is responsible for initiating regulated cell death (“apoptosis”), or cell cycle arrest when a cell is damaged. A mutated p53 gene may contribute to uncontrolled cellular proliferation, leading to a tumor. The hypothesis that SV40 might cause cancer in human has been a particularly controversial area of research. Some research has suggested that SV40 is associated with brain tumors, bone cancers, non-Hodgkin lymphoma and malignant mesothelioma. SV40 may act as a cocarcinogen with crocidolite to cause mesothelioma.
Composition: anti-human SV40 mouse monoclonal antibody purified from ascites fluid by chromatography. Prepared in 10mM PBS, pH 7.4, with 0.2% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide.
Immunogen:A synthetic peptide corresponding to residues on the N terminus of human Survivin protein.
-
آنتی بادیهای ایمونوهیستوشیمی
آنتی بادی Survivin (EP119)
Rated 0 out of 5Name: Survivin Antibody (Clone EP119)
Description and applications: Survivin is a unique member of the inhibitor of apoptosis (IAP) protein family that interferes with post-mitochondrial events including activation of caspases. Survivin regulates the cell cycle and is expressed in most tumors, but it is barely detectable in terminally differentiated normal cells and tissues. Survivin is expressed in the G2/M phase of the cell cycle. At the beginning of mitosis, surviving associates with microtubules of the mitotic spindle in a specific and saturable reaction that is regulated by microtubule dynamics. Disruption of survivin-microtubule interactions results in loss of survivin’s anti-apoptotic function and increased caspase-3 activity, a mechanism involved in cell death during mitosis.Nuclear-cytoplasmic shuttling of survivin is controlled by nuclear export signal (NES), which is necessary for the anti-apoptotic function of survivin. Inhibition of the NES makes cells more susceptible to chemotherapy- or radiotherapy-induced apoptosis. The association of survivin expression with tumor progression, but not overall patient survival, has been observed in a variety of malignancies including renal cell carcinoma, ovary carcinoma, hepatocellular carcinoma, prostate carcinoma and breast carcinoma. However, the link between a poor prognosis and nuclear expression of Survivin in tumors is controversial. A literature review of 19 publications that measured nuclear survivin in different cancer types showed the following: 9 studies concluded that nuclear survivin was associated with an unfavorable prognosis, whereas 5 showed a favorable prognosis. The authors concluded that the nuclear pool of survivin is involved in promoting cell proliferation in most (if not all) cases, whereas the cytoplasmic pool of survivin may participate in controlling cell survival but not cell proliferation.
Composition:Anti-human Survivin rabbit monoclonal antibody purified from serum and prepared in 10mM PBS, pH 7.4, with 0.2% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide.
Immunogen:A synthetic peptide corresponding to residues on the N terminus of human Survivin protein.
-
آنتی بادیهای ایمونوهیستوشیمی
آنتی بادی SOX-2 (SP76)
Rated 0 out of 5Name: SOX-2 Antibody (Clone SP76)
Description and applications: Sex determining region Y-box 2 (SOX-2) is a stem cell marker and a transcription factor expressed in basal cells of the prostate, myoepithelial cells of the breast, squamous epithelium, and fetal neural cells. Recent studies show that SOX-2 is highly expressed in some human cancers such as prostate, lung, breast, and ovarian cancers. SOX2 is a sensitive marker of
embryonal carcinoma.Composition: Anti-human SOX-2 rabbit monoclonal antibody purified from serum and prepared in 10mM PBS, pH 7.4, with 0.2% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide.
Immunogen: Synthetic peptide corresponding to Nterminus of human SOX-2 protein.
-
آنتی بادیهای ایمونوهیستوشیمی
آنتی بادی Smoothelin (R4A)
Rated 0 out of 5Name: Smoothelin Monoclonal Antibody (Clone RA4)
Description and applications: The cytoskeletal protein smoothelin is highly conserved among vertebrates and is expressed
exclusively by contractile smooth muscle cells where it localizes to the filament network. Smoothelin associates with Actin stress fibers but does not interact with Desmin. At least two isoforms of smoothelin are produced by alternative splicing. The short isoform lacks amino acids 1–544 at the amino terminus of the long isoform. The short isoform is expressed in visceral muscle tissue including intestine and stomach but not in brain, while the long isoform is expressed in all vascularized organs. In the vascular system, smoothelin expression is limited to large veins and arteries capable of pulsatile contraction. As a marker for the highly differentiated
contractile smooth muscle cell, smoothelin expression is useful for studying vascular malformation and injury. The gene encoding human smoothelin maps to chromosome 22q12.3.Composition: Anti-human Smoothelin mouse monoclonal antibody purified from serum and prepared in 10mM PBS, pH 7.4, with 0.2% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide.
-
آنتی بادیهای ایمونوهیستوشیمی
آنتی بادی AMACR/p504s (13H4)
Rated 0 out of 5Name: AMACR/p504s (13H4)
Description and applications: The main use of the combination of both antibodies in a single reagent is simultaneously immunostain prostate glands in order to detect whether or not neoplastic. In the case of prostate adenocarcinoma, neoplastic glands must present cytoplasmic staining produced by expression of p504s and absence of nuclear staining as these glands lack basal cells and thus are negative for p63. Normal or hyperplastic glands must present nuclear staining in the basal cell layer. The
Due to the different pattern of staining of the antibodies included in the cocktail, the detection could be realised with a polyvalent HRP detection systems.
Nevertheless, as the antibodies are developed in two different host, a dual detection system can be used.
Composition: anti-human AMACR/p50s rabbit monoclonal antibody + anti-human p63 mouse monoclonal antibody prepared in 10mM PBS, pH 7.4, with 0.2% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide.
Immunogen: Human AMACR polypeptide + aminoacids 1-250 of the N-terminal portion of the human p63 protein
-
آنتی بادیهای ایمونوهیستوشیمی
آنتی بادی CD8 (SP16)
Rated 0 out of 5Name: CD8 Antibody (Clone SP16)
Description and applications: CD8 molecule consists of two chains, termed α and β chain, which are expressed as a disulphide-linked α/β heterdimer or as an α/α homodimer on T cell subset, thymocytes and NK cells. The majority of CD8+ T cells express CD8 as α/β heterdimer. CD8 functions as a co-receptor in concert with TCR for binding the MHC class I/peptide complex. The HIV-2 envelope glycoprotein binds CD8 α chain (but not β chain). Along with other markers of T cells, CD8 it is used to establish diagnostic of T cell leukemias and lymphomas. The antibody is useful to ensure the origin of the lymphoid infiltrates present in biopsies and to distinguish reactive and neoplastic T cells.
Composition: anti-human CD8 rabbit monoclonal antibody purified from serum and prepared in 10mM PBS, pH 7.4, with 0.2% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide.
Immunogen: Synthetic peptide corresponding to C-terminus of alpha chain of the human CD8 molecule.