| Clone | QR066 |
|---|---|
| REF | C-G002 |
| Dilution | 1:100 – 1:200 |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human GFAP |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Species of origin | Rabbit |
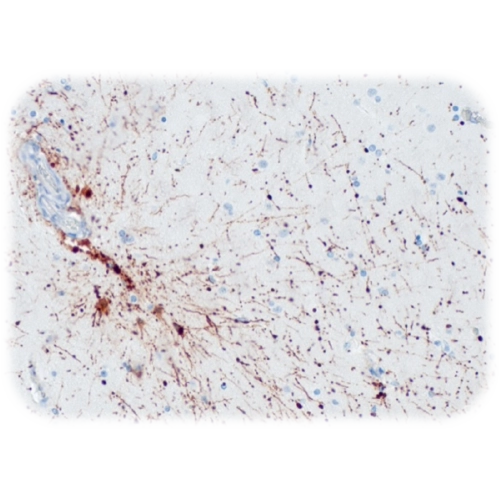
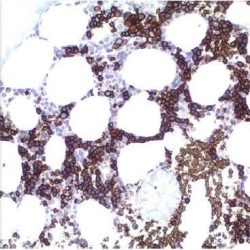
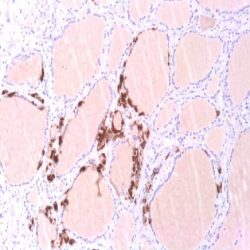
Glial fibrillary acidic protein is an intermediate filament protein that is expressed by numerous cell types of the central nervous system. In the central nervous system, GFAP is expressed in astrocytes and ependymal cells but not in other glial cells. However, immature oligodendrocytes and immature choroid plexus cells may be GFAP positive. In the peripheral nervous system enteric Schwann cells and satellite cells of human sensory ganglia express GFAP. Outside the nervous system, GFAP is seen in myoepithelial cells and chondroblasts, in the former coexpressed with cytokeratin, in the latter coexpressed with vimentin. Astrocytoma, ependymoma, glioblastoma, and oligodendroglioma are almost always positive. Plexus carcinoma, ganglioglioma and primitive neuroectodermal tumours (PNET: neuroblastoma a.o.) express GFAP to a varying extent. Schwannoma and neurofibroma frequently express GFAP. Chondroma, chondrosarcoma and pleomorphic adenoma are also GFAP positive in most cases. A few carcinomas (especially from lung and breast) may express GFAP. in paraganglioma GFAP may be detected in sustentacular cells. This marker is mainly used to distinguish neoplasms of astrocytic origin from other neoplasms in the central nervous system.