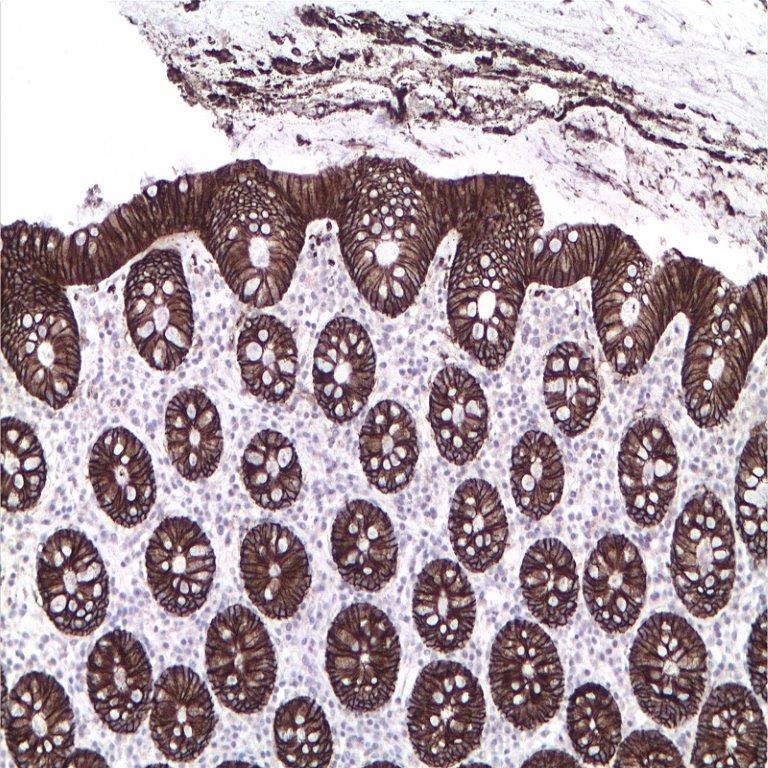
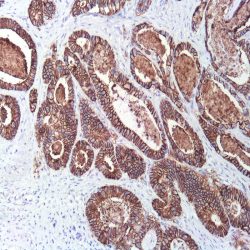
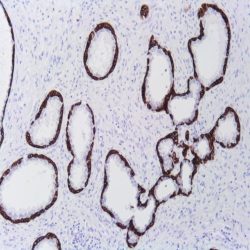
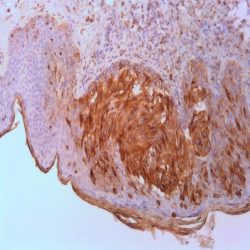
Name: Claudin-7 Antibody (Polyclonal)
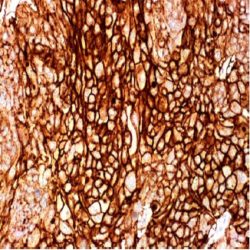
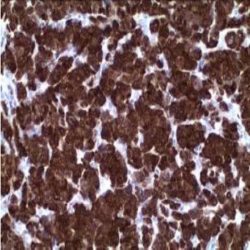
Description and applications: The claudin protein family consists of 24 different cellcell adhesion molecules that constitute the fundamental core of tight junctions, which are in charge of controlling the molecule flow between epithelial cells. This control is performed by creating a biochemical barrier against water and restricting lateral diffusion of membrane lipids and proteins towards the paracellular spaces between the apical and the basement membrane, which, however, allows polar molecule transport. This antibody recognises claudin 7, whose expression is controlled by a gene located on chromosome 17. In addition to the general metabolic control functions described above for claudins, claudin 7, specifically in its phosphorylated form: 1) interacts with EPCAM by regulating its expression; 2) promotes E-cadherin normal expression by epithelial cells; and 3) regulates the expression of prostate-specific antigen (PSA) and is involved in the androgen receptor regulation mechanism. In this sense, its maximum expression takes place in tissues with normal levels of dihydrotestosterone (DHT), while high concentrations of this molecule inhibit its presence. Claudin 7 is frequently expressed in the distal nephron epithelium, prostate, airway epithelium, and other glandular-type epithelia where it shows membrane staining. CNS cells and lymphoid cells are negative. Claudins are present in a variety of normal, hyperplastic, and benign tissues as well as in benign and malignant neoplasms that show epithelial differentiation. It is for this reason that the differential expression of its different members can be used to confirm the histological identity of some neoplasms. Thus, claudin immunohistochemical detection, including claudin 7, makes it possible to differentiate and confirm the diagnosis between: 1) oncocytomas and chromophobe cell renal carcinomas; 2) endometrioid carcinoma and uterine papillary serous carcinoma; 3) mesothelioma and adenocarcinoma metastasis; 4) hepatocellular carcinoma and cholangiocarcinoma; and 5) diffuse and intestinal-type gastric carcinomas. Its usefulness has also been shown for distinguishing between highgrade ductal in situ and lobular carcinomas, and infiltrating carcinomas of the breast. In addition, its cytoplasmic expression in solid pseudopapillary tumours of the pancreas enables the differential diagnosis with other tumours such as pancreatoblastoma, acinar cell carcinoma, or pancreatic neuroendocrine tumours since all of them show membrane staining for claudin 7. Similarly, the expression of certain claudins can be used as a prognostic marker in various neoplasms such as nasopharyngeal carcinomas, where claudin 7 overexpression correlates with tumour grade, presence of distant metastases, and survival. Similar results have been obtained in ovarian adenocarcinomas. Likewise, an increase in the expression of claudins 1 and 7 has also been detected in cervical premalignant lesions and invasive neoplasms compared to normal epithelium.
Composition: anti-human Claudin-7 rabbit polyclonal antibody purified from serum and prepared in 10mM PBS, pH 7.4, with 0.2% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide.
Immunogen: Synthetic peptide corresponding to the C-terminal domain of human claudin 7.

Reviews
There are no reviews yet.