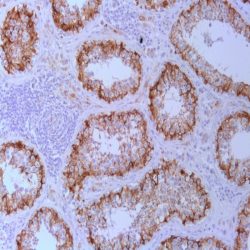
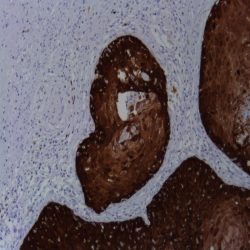
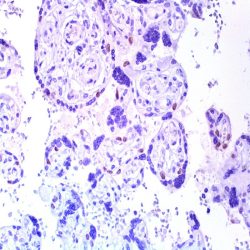
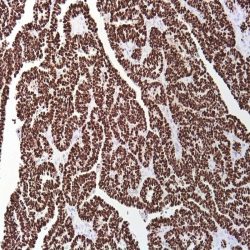
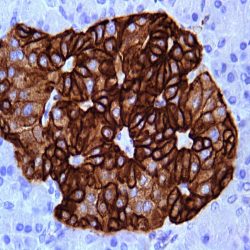
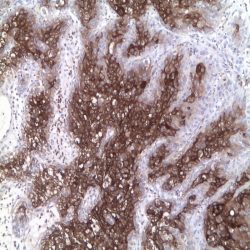
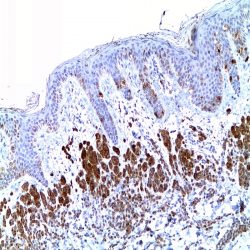
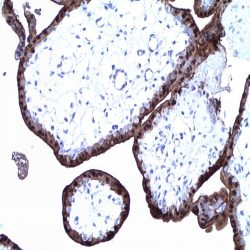
Category: immunohistochemistry
Showing 201–220 of 391 results
فیلتر ها-
آنتی بادیهای ایمونوهیستوشیمی
آنتی بادی Oct3/4 (C-10)
Rated 0 out of 5Name: Mouse Anti-OCT 3/4 Monoclonal Antibody
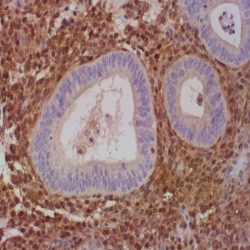
Description and aplications: OCT-3 (officially POU5F1, also known as OCT4, OCT 3/4, OTF3 or OTF4) is a nuclear transcription factor involved in the initiation, maintenance and differentiation of germ cells and stem cells during embryonic development. The antibody recognizes a protein of 18kDa molecular weight encoded by the gene POU5F1 located on chromosome 6p21.3 which is essential in the development of the blastocyst. Three isoforms of OCT-3-called OCT-3A, OCT-3B and OCT3B1 are generated by alternative splicing. Isoforms A and B1 are expressed only in germ cell tumors while OCT3B isoform may also be expressed in tumors of somatic origin. This antibody is useful for the identification of transcription factor OCT-3/4 present in normal tissues (embryonic testis) and neoplastic ones. Gonadoblastomas, intratubular germ cell tumors, testicular seminoma, ovarian dysgerminomas, extragonadal germinomas and embryonal carcinoma show nuclear positivity with different degrees of intensity. By contrast the yolk sac tumors, spermatocytic seminomas, choriocarcinoma, testicular and ovarian teratomas are negative. Its expression has also been demonstrated in several tumor lines of somatic origin and linked to poor prognosis
Composition: anti-OCT3/4 mouse monoclonal antibody obtained from supernatant culture and prediluted in a tris buffered solution pH 7.4 containing 0.375mM sodium azide solution as bacteriostatic and bactericidal.
Immunogen: amino acids 1-134 of Oct-3/4 of human origin
-
آنتی بادیهای ایمونوهیستوشیمی
آنتی بادی Mucin 5AC (MUC5AC) (MD-19 also known as MRQ-19)
Rated 0 out of 5Name: Mucin 5AC (MUC5AC) Antibody (Clone MUC5AC, MD-19 also known as MRQ-19)
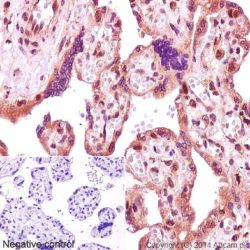
Description and applications: Mucins are glycoproteins of high molecular weight linked to oligosaccharides in the threonine or serine wastes by glycosidic bonds produced by different epithelial cells. In humans, at least 14 genes coding for mucins have been identified (MUC1, MUC2, MUC3, MUC4, MUC5AC, MUC5B, MUC6, MUC7, MUC8, MUC9, MUC11, MUC12, MUC13 and MUC16). Mucins are classified as follows: Membrane-bound mucins (MUC1, MUC3, MUC4, MUC12 and MUC16), secreted mucins forming gel-like secretion (MUC2, MUC5AC, MUC5B, and MUC6) and secreted soluble mucin (MUC7). Mucins are the main component of the mucous membrane that protects the gastric mucosa from the chemical and mechanical insults. This antibody reacts with the mucin 5AC. MUC5AC isthe glycoprotein secreted forming gel-like secretions expressed by the gastric epithelium and the respiratory tract. The distribution of the expression of the mucins is heterogeneous MUC1 (stomach and pancreas), MUC2 (small and large intestine), MUC4 (stomach), MUC5AC (stomach) and MUC6 (stomach, small intestine and pancreas). MUC5AC is expressed in apical rim in normal cells and also in the lateral edges of the cytoplasmic membrane and intracytoplasmically in carcinomas of different tissues. MUC5AC is expressed in normal gastric epithelium in the cardia, fundus and pyloric antrum. Barrett’s esophagus shows positivity for this mucin; MUC5AC is not expressed in the small intestine, large intestine nor pancreas. In neoplastic tissues, it is expressed in pancreatic, colon and appendix adenocarcinomas, extramammary Paget’s disease Colloid carcinomas of the breast nor cholangiocarcinomas in general do not express MUC5AC. The mucin expression pattern in tumors has been associated with the tumor location, the biological insult and the infiltration capacity of some neoplasias.
Composition: Anti-human Mucin 5AC mouse monoclonal antibody purified from serum and prepared in 10mM PBS, pH 7.4, with 0.2% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide.
-
آنتی بادیهای ایمونوهیستوشیمی
آنتی بادی Mucin 2 (Ccp 58)
Rated 0 out of 5Name: Mucin 2 (MUC-2) Antibody (Clone Ccp58)
Description and applications: Secreted epithelial mucins are large macromolecules which exhibit extreme polydispersity. Mucin 2 is the major intestinal mucin. O-glycans are attached to MUC2 in a potentially diverse arrangement, which is crucial for their interaction with endogeneous and exogeneous lectins. MUC2 is expressed in glandular epithelium (goblet cells) of normal small and large intestine, Barrett’s esophagus and breast glandular epithelium; it is not expressed in stomach or pancreas. In neoplastic tissues the pattern of mucins expression in tumours has been associated with tumor location, the biological aggressiveness and the infiltration capacity of certain malignancies. MUC2 is expressed by colon and appendix signet ring adenocarcinomas, breast colloid carcinoma, Paget’s disease of the breast and prostate carcinoma. It is not expresses by endometrial carcinomas, the non-mucinous breast or pancreatobiliary carcinomas.
Composition: anti-human MUC-2 mouse monoclonal antibody purified from serum and prepared in 10mM PBS, pH 7.4, with 0.2% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide.
-
آنتی بادیهای ایمونوهیستوشیمی
آنتی بادی Mucin 6 (MD-20 also known as MRQ-20)
Rated 0 out of 5Name: Anti-Mucin 6 (MUC6) Antibody (Clone MRQ-20)
Description and aplications: Mucins are high molecular weight glycoproteins produced by epithelial cells. In humans, at least 14 genes encoding mucin has been identified (MUC1, MUC2, MUC3, MUC4, MUC5AC, MUC5B, MUC6, MUC7, MUC8, MUC9, MUC11, MUC12, MUC13 and MUC16). Mucins are classified as membrane associated (MUC1, MUC3, MUC4, MUC12 and MUC16), secreted mucins forming gels (MUC2, MUC5AC, MUC5B, and MUC6), or soluble secreted mucin (MUC7). Mucins are the major component of the mucus layer which protects against chemical and mechanical gastric mucosa aggression. MUC6 is expressed in the normal gastric epithelium of the pyloric antrum, in Brüner duodenal glands, small intestine, and pancreas; MUC6 is not expressed in ducts or acini of normal breasts or Barrett’s esophagus. In neoplastic tissues MUC6 is expressed in colloidal breast carcinomas. Breast carcinomas, pancreatic adenocarcinomas and cholangiocarcinomas do not express MUC6. The pattern of mucin expression in tumors has been associated with tumor location, the biological aggressiveness, and the infiltration capacity of certain malignancies.
Composition: anti-MUC-6 mouse monoclonal antibody obtained from supernatant culture and prediluted in a tris buffered solution pH 7.4 containing 0.375mM sodium azide solution as bacteriostatic and bactericidal.
-
آنتی بادیهای ایمونوهیستوشیمی
آنتی بادی Olig 2 Protein (211F1.1)
Rated 0 out of 5Name: Olig 2 Protein Antibody-Clone 211F1.1
Description and applications: Olig2, a basic helix–loop–helix transcription factor, is involved in oligodendroglial specification. Olig2 expression has been reported in most glial tumors, such as oligodendrogliomas and astrocytomas. Although more than half of glioblastomas are positive for Olig2, expression is very weak in terms of both percentage of labeled cells and intensity. No Olig2 expression has been found in the non-glial tumors including neuroepithelial tumors, ependymomas, subependymomas, medulloblastomas, and nonneuroepithelial tumors, such as CNS lymphomas, meningiomas, schwannomas, atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumor, and haemangioblastomas. Compared to the strong staining seen in glioma samples, a weak expression is observed in nontumoral brain tissue (gliosis). In order to characterize cellular subtypes that constitute astrocytomas, oligoastrocytomas and oligodendrogliomas, double labeling of Olig2 and GFAP has been performed which identified two phenotypically distinct tumor populations. The first is Olig2+/GFAP– which has an oligodendroglial morphology, corresponding to pure oligodendrogliomas that contain only oligodendroglial cells; the second is Olig2–/GFAP+ which has an astrocytic phenotype, including not only oligoastrocytomas, but also WHO astrocytomas. Depending on proportion and spatial clustering of the two phenotypically distinct tumor populations, the tumor (Olig2-/GFAP+) is classified either as an astrocytoma when both populations are intermingled with a dominance of GFAP+ cells or oligoastrocytoma when there is some degree of spatial clustering of the GFAP+ cells.
Composition: anti-human Olig 2 protein mouse monoclonal antibody purified from serum and prepared in 10mM PBS, pH 7.4, with 0.2% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide.
-
آنتی بادیهای ایمونوهیستوشیمی
آنتی بادی MUM1/IRF4 (MUM1p)
Rated 0 out of 5Name: MUM1 Antibody (Clone MUM1p)
Description and aplications: MUM1 / IRF4 is an oncogene associated with myeloma. The protein has a molecular weight of 51.6 kDa and is encoded by a gene on chromosome 6p25-p23 region located mainly in the nucleus of lymphocytes. When MUM1 is not expressed, the B / T cells do not get activated and the immunoglobulins are not secreted by the plasma cells. Most neoplasms composed of mature lymphoid cells express MUM1. Therefore, this protein is expressed in a subset of B cells in the germinal center in plasma cells and in activated T cells. MUM1 is a marker that helps in characterizing the histogenesis of lymphoma / leukemia of B origin. In Bcell lymphomas, MUM1 expression presents a predictive role of the genetic profile and represents, together with CD10 and BCL-6, the base of Hans classification for diffused large B cell lymphomas. MUM1 positivity, in these cases, suggests a non-germinal center phenotype and is predictive for prognosis, especially in pediatric cases. In Burkitt lymphomas, that shares cytological, architectural and histological aspects with some cases of DLBCL of “Burkitt-like”, the MUM1 is negative in general or positive in a small percentage of cases or tumoral cells. All cases of primary effusion lymphomas and most cases of primary brain lymphomas are MUM1 positive. Other lymphoid neoplasm express MUM1. Melanomas can also stain with MUM1.
Composition: anti-MUM1 mouse monoclonal antibody obtained from supernatant culture and prediluted in a tris buffered solution pH 7.4 containing 0.375mM sodium azide solution as bacteriostatic and bactericidal.
-
آنتی بادیهای ایمونوهیستوشیمی
آنتی بادی Lambda Inmunoglobulin Light Chain (EP172)
Rated 0 out of 5Name: Lambda light chain Antibody (Clone EP172)
Description and applications: Each immunoglobulin molecule consists of two identical heavy chains and two identical light chains. There are two types of light chains designated as kappa and lambda. The gene rearrangement process that generates the immunoglobulin molecule results in either a productive kappa or lambda gene. The mechanics of the rearrangement process normally produce approximately twice as many kappa-bearing cells as lambda. However this ratio is lost during malignant transformation. The kappa light chain antibody labels kappa light chain expressing B lymphocytes and plasma cells. Other cells may also express kappa light chain due to nonspecific uptake of immunoglobulin.
Composition: anti-human Lambda light chain rabbit monoclonal antibody purified from serum and prepared in 10mM PBS, pH 7.4, with 0.2% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide.
-
آنتی بادیهای ایمونوهیستوشیمی
آنتی بادی Kappa Immunoglobulin Light Chain (EP171)
Rated 0 out of 5Name: Kappa light chain Antibody (Clone EP171)
Description and applications: Each immunoglobulin molecule consists of two identical heavy chains and two identical light chains. There are two types of light chains designated as kappa and lambda. The gene rearrangement process that generates the immunoglobulin molecule results in either a productive kappa or lambda gene. The mechanics of the rearrangement process normally produce approximately twice as many kappa-bearing cells as lambda. However this ratio is lost during malignant transformation. The kappa light chain antibody labels kappa light chain expressing B lymphocytes and plasma cells. Other cells may also express kappa light chain due to nonspecific uptake of immunoglobulin. Individual B cells express either kappa or lambda light chains. Monoclonality is generally assumed to be evidence of a malignant proliferation. The pairing of an antilambda with a kappa light chain antibody is useful for identifying monoclonality of lymphoid malignancies.
Composition: anti-human Kappa light chain rabbit monoclonal antibody purified from serum and prepared in 10mM PBS, pH 7.4, with 0.2% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide.
-
آنتی بادیهای ایمونوهیستوشیمی
آنتی بادی Osteocalcin (G5)
Rated 0 out of 5Name: Osteocalcin Antibody-Clone G5
Description and applications: Bone γ carboxyglutamic acid (Gla) protein, known as BGLAP, BGP or osteocalcin, is an abundant, non-collagenous protein component of bone that is produced by osteoblasts. In mice, osteocalcin is composed of a cluster of three genes known as OG1, OG2 and ORG, all of which can be found within a 23 kb span of genomic DNA. Human osteocalcin is a highly conserved, 46-50 amino acid, single chain protein that contains three vitamin K-dependent γcarboxyglutamic acid residues. Osteocalcin appears transiently in embryonic bone at the time of mineral deposition, where it binds to hydroxyapatite in a calcium-dependent manner. In addition, osteocalcin is one of the most abundant, non-collagenous proteinsfound in mineralized adult bone. Genetic variation at the osteocalcin locus on chromosome 1q impacts postmenopause bone mineral density (BMD) levels and may predispose some women to osteoporosis.
Composition: Anti-human Osteocalcin rabbit polyclonal antibody purified from serum and prepared in PBS with < 0.1% sodium azide and 0.1% gelatin.
IMMUNOGEN: antibody raised against amino acids 1-100 representing full length osteocalcin of human origin.
-
آنتی بادیهای ایمونوهیستوشیمی
آنتی بادی p16-INK4 (MX007)
Rated 0 out of 5Name: P16 INK4A Antibody-Clone MX007
Description and applications: As one of the cyclindependent kinase inhibitors that inhibit cylcindependent kinases 4 and 6, p16 INK4A is encoded by tumor suppressor gene CDKN2A. The tumor suppressor p16 INK4A plays an important role in cell cycle regulation. Increased expression of the p16 gene, which is seen as organisms ages, reduces the proliferation of stem cells. This reduction in the division and production of stem cells protects against cancer while increasing the risks associated with cellular senescence. Mutations in the p16 gene associated with loss or over expression of the protein are associated with increased risk of a wide range of cancers and cancer precursor lesions. The immunohistochemical identification of p16 is particularly relevant in uterine cervical lesions. Development of dysplasia is closely related to human papilloma virus (HPV) infection. Although the frequency of p16INK4a abnormalities is higher in tumor-derived cell lines than in unselected primary tumors, significant subsets of clinical cases with aberrant p16INK4a gene have been reported among melanomas, gliomas, esophageal, pancreatic, lung, and urinary bladder carcinomas, and some types of leukemia.
Composition: anti-human p16INK4A mouse monoclonal antibody purified from serum and prepared in 10mM PBS, pH 7.4, with 0.2% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide.
-
آنتی بادیهای ایمونوهیستوشیمی
آنتی بادی P40 (ZR8)
Rated 0 out of 5Name:Anti-human p40Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody (Clone ZR8)
Description and applications: P63 consists of two major isoforms-TAp63 and ΔNp63. These isoforms differ in the structure of the Nterminal domains. The TAp63 isoform (identified by anti-p63 antibody) contains a transactivation-competent ‘TA’ domain with homology to p53, which regulates the expression of the growth-inhibitory genes. In contrast, ΔNp63 isoform (identified by anti-p40 antibody) contains an alternative transcriptionally-inactive ‘ΔN’ domain, which antagonizes the activity of TAp63 and p53. The p40 (clone ZR8) antibody recognizes exclusively ΔNp63 but not TAp63. p40 is a squamous cell carcinoma ‘specific’ antibody. It reacts with the vast majority of cases of squamous cell carcinomas of various origins, but not with adenocarcinomas. It is particularly useful in differentiating lung squamous cell carcinoma from lung adenocarcinoma. p40 antibody can also be used as an alternative basal cell/myoepithelial cell marker, which has similar sensitivity and specificity as that of p63 antibody. Therefore, p40 antibody may also be used as an alternative immunohistochemical markerfor determining prostate adenocarcinoma vs. benign prostate glands and for determining breast intraductal carcinoma vs. invasive breast ductal carcinoma.
Composition: anti-human p40 rabbit monoclonal purified antibody in 0.2% BSA and 15mM sodium azide.
Immunogen: Synthesized polypeptides from Nterminal domain of p63.
-
آنتی بادیهای ایمونوهیستوشیمی
آنتی بادی p53 (SP5)
Rated 0 out of 5Name: Rabbit anti-human p53 Monoclonal Antibody
Description and applications: p53 is a tumour suppressor gene expressed in a wide variety of tissue types and is involved in regulating cell growth, replication, and apoptosis. The p53 gene is located on chromosome 17p, a frequent location in the loss of alleles in many tumors such as lung, colon, breast and brain. p53 expression is associated with a poor prognosis in breast cancer. In colon tumors, the p53 protein is expressed in 47% of cancers and only 9% of adenomas. In addition, p53 mutations are associated with a large number of malignant tumors, including ovarian, bladder and melanomas.
Composition: anti-human p53 rabbit monoclonal antibody purified from ascites. Prepared in 10mM PBS, pH 7.4, with 0.2% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide
Immunogen: Recombinant human full length wild type p53 protein
-
آنتی بادیهای ایمونوهیستوشیمی
آنتی بادی PTEN (6H2.1)
Rated 0 out of 5Name: PTEN Antibody (Clone 6H2.1)
Description and aplications: The antibody recognizes a protein fraction of 403 amino acids encoded by the PTEN gene located on chromosome 10q23.3 region. PTEN protein acts as a dual specificity phosphatase. On one hand, it dephosphorylates the phosphorylated proteins in tyrosine, serine, and threonine residues and on the other hand, it acts as a lipid phosphatase removing the phosphate group of the D3 position of the inositol ring in phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate, phosphatidylinositol-3,4-diphosphate, phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate, and inositol 1,3,4,5- tetrakisfosfato. This last feature is critical to act as a tumor suppressor through the negative regulation of the signaling pathway PI3K-AKT / PKB. This latter controls cell cycle progression, the tissue development, cell migration, and inhibition of apoptosis. In this signaling pathway, PTEN antagonistic effect on PI3K-AKT / PKB also maintains the stability of p53. PTEN also controls other cell cycle proteins such as p27, p130, myc, and cyclin D1. PTEN gene mutations induce alterations in the functioning of cells in a manner that the loss of PTEN protein expression is associated with tumor genesis, cancer progression, and cancer-resistance to different
treatments. Due to its role in cell growth, the vast majority of normal tissues express high amount of the PTEN protein. The loss of PTEN protein expression was observed in some malignancies associated with abnormalities in the PTEN gene. These abnormalities
can be monoallelic (gliomas and carcinomas of breast, prostate, lung, and colon) or biallelic (endometrial carcinomas, prostate and breast cancer, or glioblastoma multiforme). There are also some genetic diseases with alterations of germinal type in the PTEN gene like Cowden syndrome, Bannayan-Riley-Ruvalcaba syndrome, Lhermitte-Duclos disease and a subgroup of patients with Proteus syndrome. Somatic mutations of PTEN with loss of protein expression present variable incidences although they are often observed in sporadic endometrial carcinomas and in glioblastoma multiforme. These mutations are usually related to the histological grade of the tumor and are considered poor prognostic factors. Loss of PTEN expression is also a prognostic factor in gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST), tumors of the salivary glands, intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma, gallbladder carcinomas, etc. In addition to being a prognostic factor, PTEN antibody immunostaining acts as a predictive indicator of the response to therapy using chemotherapeutic agents aimed at molecular targets. Controversial results obtained with the PTEN antibody are apparently related to the antibody clone used and/or tissue fixation issues. The only clone with reproducible results in the diagnosis of paraffin embedded samples, especially in endometrial adenocarcinomas and their precursor lesions, is the 6H2.1. However, superior results are always obtained in excisional biopsy or curettage samples in comparison with immunostaining of hysterectomies samples, where fixing is usually worse. In this sense and to mitigate immunostaining loss it is recommended to use freshly obtained serial sections of the sample.Composition: anti-PTEN mouse monoclonal antibody obtained from supernatant culture and prediluted in a tris buffered solution pH 7.4 containing 0.375mM sodium azide solution as bacteriostatic and bactericidal.
-
آنتی بادیهای ایمونوهیستوشیمی
آنتی بادی p57 (KP10 same as 57P06)
Rated 0 out of 5Name: Mouse anti-human p57kip2 Monoclonal Antibody
Description and applications: p57Kip2 (or CDKN1C) is a potent tight-binding inhibitor of several G1 cyclin complexes, and is a negative regulator of cell proliferation. The gene encoding human p57Kip2 is located on chromosome 11p15.5, a region implicated in both sporadic cancers, Wilm’s tumor, and Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome (BWS), a cancer syndrome, making it a tumor suppressor candidate. BWS is characterized by numerous growth abnormalities and an increased risk of childhood tumors. Several types of childhood tumors including Wilms’ tumor, adrenocortical carcinoma and rhabdomyosarcoma display a specific loss of maternal 11p15 alleles, suggesting that genomic imprinting plays an important part. This region also contains two other imprinted genes, insulin-like growth factor II (IGF-II) and H19, both of which seem to be implicated in adrenal neoplasms. The practical use of p57kip2 antibody resides in the differential diagnosis of complete hydatidiform mole (comprised solely of paternal DNA and consequently with lack of nuclear expression in the cytotrophoblast and villous stromal cells), the incomplete hydatidiform mole (triploid) and edematous abortion. Extravillous trophoblastic islets, maternal decidua and stromal cells of the villi serve as internal controls in all three entities. The syncytiotrophoblast is negative in all cases.
Composition: anti-human p57kip2 mouse monoclonal antibody purified from serum and prepared in 10mM PBS, pH 7.4, with 0.2% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide
Intended use : Immunohistochemistry (IHC) on paraffin embedded tissues. Not tested on frozen tissues or Western-Blotting
Immunogen: Recombinant human p57Kip2 protein.
-
آنتی بادیهای ایمونوهیستوشیمی
آنتی بادی PTH (Parathyroid Hormone) (77/78)
Rated 0 out of 5Name: Parathyroid Hormone (PTH) clone 77/78
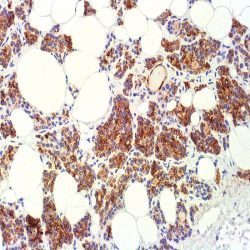
Description and aplications: The PTH is a major regulator of serum calcium and is essential for life, unlike calcitonin , which acts as a complementary regulatory mechanism . Chromophobe cells responsible for the secretion of PTH, are the most abundant in the gland. This antibody is useful for immunohistochemical detection of parathyroid hormone, and used in conjunction with antibodies to thyroglobulin allows the differential diagnosis of lesions of thyroid and parathyroid origin .
Composition: anti- parathyroid hormone (PTH) mouse monoclonal antibody obtained from supernatant culture and prediluted in a tris buffered solution pH 7.4 containing 0.375mM sodium azide solution as bacteriostatic and bactericidal. The quantity of the active antibody was not determined.
-
آنتی بادیهای ایمونوهیستوشیمی
آنتی بادی PU-1 (EP18)
Rated 0 out of 5Name: Antibody PU-1
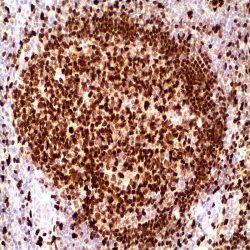
Description and applications: This antibody recognises a protein with a molecular mass of 42 kDa corresponding to PU.1 transcription factor, a member of the Ets family of transcription factors. It is required for the normal development and maturation of multiple hematopoietic lineages. PU.1 is a transcription factor restricted to the hematopoietic system, expressed in the myeloid series and in B cells but absent in mature T cells, the erythroid series, and in non-hematopoietic cells. Among the cells of the myeloid series, PU.1 is overexpressed in monocytes, histiocytes, and dendritic cells. Nodular lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin lymphoma is consistently positive for PU.1, as opposed to classical Hodgkin lymphoma; therefore, PU.1, along with Pax-5, Oct-1, Oct-2, and BOB.1, is useful in establishing the differential diagnosis between both entities. PU.1 transcription factor and AML1, a DNAbinding subunit of the CBF transcription factor family, act as tumour suppressors in leukaemias. The function of PU.1 is down-regulated by AML1-ETO in myeloid leukaemias, while overexpression of PU.1 restores normal differentiation. High expression of PU.1 in follicular lymphomas gives them greater survival. PU.1 is a suitable marker to identify cutaneous neoplasms originating from histiocytes or from dendritic cells (reticulohistiocytomas, Langerhans cell histiocytosis, or juvenile xanthogranulomas).Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans, dermatofibromas, fibrous papules, Spitz nevi, and melanomas are not stained with anti-PU.1.
Composition:Anti-human PU-1 rabbit monoclonal antibody purified from serum and prepared in 10mM PBS, pH 7.4, with 0.2% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide
Intended use : Immunohistochemistry (IHC) on paraffin embedded tissues. Not tested on frozen tissues or Western-Blotting
-
آنتی بادیهای ایمونوهیستوشیمی
آنتی بادی Retinoblastoma/pRb (1F8)
Rated 0 out of 5Name: Antibody Retinoblastoma clone same as Rb1) 1F8
Description and applications: Rb is a tumor suppressor nuclear phosphoprotein capable of binding to DNA. It is phosphorylated on serine and threonine, but not on tyrosine residues. It forms a complex with SV40 large T antigen, adenovirus E1A and human papilloma virus-16 E. Rb protein may act by regulating transcription and loss of its function leads to uncontrolled cell growth. 90% of neoplasias express moderately or intensely pRb (carcinomas of the breast, colon, stomach, endometrium, head and neck, lung, neuroendocrine, gliomas, lymphomas, melanoma, ovarian, pancreatic, kidney, urothelial, cutaneous and thyroid). The alteration of the Rb gene with the absence of nuclear expression of pRb has been demonstrated in some human tumors, including retinoblastoma, breast carcinoma, prostate cancer, lung cancer and some sarcomas.
Composition: Anti-human Retinoblastoma mouse monoclonal antibody purified from serum and prepared in 10mM PBS, pH 7.4, with 0.2% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide
-
آنتی بادیهای ایمونوهیستوشیمی
آنتی بادی S100 Protein (4C4.9)
Rated 0 out of 5Name: Antibody S100 Protein clone 4C4.9
Description and aplications:
S100 belongs to the family of calcium binding proteins such as calmodulin and troponin C. S100A is composed of an alpha and beta chain whereas S100B is composed of two beta chains. S100 protein is also expressed in the antigen presenting cells such as the Langerhans cells in skin and interdigitating reticulum cells in the paracortex of lymph nodes. The S100 antibody staines schwannomas, ependymomas, astrogliomas, most melanomas and their metastases. It is also characteristic in adipose and chondroid tissue benign and malignant neoplasms. It can also be used as a myoepithelial marker for breast pathology diagnostic. Therefore, this antibody is useful for the identification of malignant melanomas, neuroectodermal, adipocytic and chondroid tumors. This antibody has a cross-reactivity with smooth muscle fibers that can be visible in some occasions.Composition: anti-human S100 Mouse monoclonal antibody purified from ascites. Prepared in 10mM PBS, pH 7.4, with 0.2% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide
-
آنتی بادیهای ایمونوهیستوشیمی
آنتی بادی S100-Beta Protein (SP127)
Rated 0 out of 5Name:Antibody S100-Beta Protein clone SP127
Description and applications: S100 proteins are a set of 25 small acidic molecules with a molecular mass of 10-12 kDa that are functionally grouped into homo or heterodimers composed of two subunits, alpha and beta, capable of combining with each other and with extensive sequence homology. There exist up to 14 variants of the alpha chain gene, which is located on chromosome 1q21; on the contrary, there is only one sequence of the beta chain gene, located on chromosome 21q22.3, showing its greater functional specificity. In its dimeric form, the S100 protein, together with calmodulin and troponin C, belongs to the calcium binding protein family; its affinity for this ion, as well as for other metals such as zinc, is remarkable. It is for this reason that the S100 protein is involved in basic cellular activities such as cation diffusion across lipid membranes, microtubule assembly, and RNA polymerase activity. In neurons, the S100 protein also regulates the interaction between chromosomes and synaptosomes. Depending on the combination between the alpha and beta single chains to form dimers and the homology of their sequences, there exist three forms of S-100 protein: A, with at least 15 subtypes between A1 and A14, B, and G. The S100-B protein is a 21-kDa beta-chain homodimer involved in the regulation of numerous processes that require calcium ion flow stimulation. The S100-B protein is present in neurons, glial cells of the central nervous system, Schwann cells and satellite cells of the peripheral nervous system (but not perineural cells), melanocytes, myoepithelial cells, glandular epithelia of the breast and the kidney, skeletal muscle and heart cells, adipocytes, and chondrocytes. This molecule is also expressed in antigen-presenting cells such as Langerhans cells of the skin, and interdigitating dendritic cells in the T-cell areas of lymphoid tissue. In contrast, the S100-B protein is not present in smooth muscle fibres. In neoplasms, the S100-B protein is highly expressed in tumours of the central and peripheral nervous systems and in melanomas, including desmoplastic melanoma. However, up to 4% of melanomas may be negative against this antibody, suggesting the need to assess this staining within a minimal panel of antimelanoma antibodies that at least includes the HMB45 and Melan A markers. Likewise and in comparison with primary lesions, some loss of expression of the S100-B protein has been observed in metastatic melanoma lesions. The S100-B protein is also useful in the diagnosis of tumours derived from cartilage, adipose tissue, and interdigitating reticular cells in lymphoid tissue, as well as granular cell peripheral nerve sheath tumours, myoepithelial tumours, paragangliomas (sustentacular cells), PEComas, Rosai-Dorfman disease, clear cell sarcoma, chordoma, adenoid cystic carcinoma, and isolated cases of synovial sarcoma and rhabdomyosarcoma. Atypical fibroxanthomas, cardiac sarcomas, myofibroblastomas, xanthomas, and solitary fibrous tumours are all negative for S100-B. Finally, altered overexpression of the beta-chain gene with S100-B protein overexpression may be found in the basis of some of the lesions observed in various types of neurological and genetic diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease, Down’s syndrome (trisomy 21), epilepsy, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, and type I diabetes, in which an excess of the S100-B protein has a potential neurotoxic effect. In this sense, several tests have been developed for serum determination of this cell damage marker in these patients.
Composition: Anti-human S100-Beta Protein rabbit monoclonal antibody purified from serum and prepared in 10mM PBS, pH 7.4, with 0.2% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide
-
آنتی بادیهای ایمونوهیستوشیمی
آنتی بادی S100-P Protein (16/F5)
Rated 0 out of 5Name: Antibody Protein S100 clone 16/F5
Composition: Anti-human S100-P Protein mouse monoclonal antibody purified from serum and prepared in 10mM PBS, pH 7.4, with 0.2% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide
Description and applications: The S100P protein, or placental S100, which is a member of the large S100 protein family, is involved in Ca2+ intracellular transport and, together with EZR and PPP5C proteins, participates in the formation of microvilli in epithelial cells and stimulates apocrine cell secretion. Unlike the genes of the other members of the S100 family of proteins, which co-localise in the 1q21 region, the S100P protein is encoded by the S100P gene, located in the 4p16 region. The 100 family of proteins is expressed in a wide range of cells, where it plays a role in cell cycle progression and in cell differentiation. The S100P molecule was initially identified in the human placenta at rather high levels. Pathologically, the antibody against the S100P protein has shown nuclear or nuclear/cytoplasmic immunoreactivity in almost all pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas, while it displays no staining in normal ducts and in pancreatic acini. In addition, the S100P protein has also been detected in virtually all pancreatic intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms, as well as in its microinvasive and diffusely invasive component, including tumours with perineural and lymphatic invasion. For both reasons, the antibody against the S100P protein is considered a useful tool for the differential diagnosis between reactive and neoplastic lesions of the pancreas. In the case of liver and bile ducts, the antibody also exhibits marked nuclear and cytoplasmic positivity in malignant lesions derived from bile ducts, while the benign epithelium derived from these tumours is negative. Similarly, detection of both S100P and GATA3 may help to distinguish urothelial carcinomas from other genitourinary neoplasms such as prostate cancers and renal cell carcinomas; in this case, however, and in contrast to what is observed in biliary and pancreatic ductal lesions, S100P expression can be detected in the normal urothelium. Finally, the anti-S100P antibody can be used as a prognostic factor in non-small cell lung carcinomas, where S100P expression has been associated with frequent distant metastases and short survival.