فروشگاه
Showing 301–320 of 605 results
فیلتر ها-
ایمونو هیستوشیمی
TBS Tween 20 Buffer 10X
Rated 0 out of 5Read moreProduct Composition: The composition of the 10x concentrated product is: Tris-HCl 500 mM, NaCl 3M, 0.5 % Tween 20, pH 7.5.
Recommendations for Use:
Before start using the product: This solution is 10x concentrated, so before its use it must be diluted
1:10 with double-distilled or deionized water (1 part of buffer and 9 parts of water). -
ایمونو هیستوشیمی
PBS BUFFER
Rated 0 out of 5Read moreProduct Composition: 10 mM Sodium/Potassium Phosphate pH 7.4, 0.9% Sodium Chloride
Recommendations for Use:
Before start using the product: The solution is concentrated, so a dilution prior to its use is required. To do this, the content of each sachet is diluted in 1 L of double-distilled or deionized water.
1- Cut and mount the sections on silane-treated slides.
2- Deparaffinize and hydrate the tissue sections.
3- Retrieval: For the retrieval process, the appropriate antigen retrieval agent is used for each antibody (specified by the manufacturer).
4.- Remove sections and place them in PBS, pH 7.40.
5.- Proceed with the immunohistochemical staining. -
آنتی بادیهای ایمونوهیستوشیمی
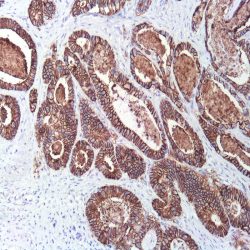
آنتی بادی Ep-CAM (EP155)
Rated 0 out of 5Read moreName: Ep-CAM/Epithelial Specific Antigen Monoclonal Antibody clone EP-155
Description and Applications: Anti-MOC-31 reacts with a transmembrane glycoprotein present on most glandular epithelium and tumors originating from such epithelium. This antibody has been used to distinguish adenocarcinoma from mesothelioma and hepatocellular carcinoma. This antibody is also useful in distinguishing serous carcinomas of the ovary from mesothelioma.
Composition: Anti-human Ep-CAM mouse monoclonal antibody purified from serum and prepared in 10mM PBS, pH 7.4, with 0.2% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide
Intended use: Immunohistochemistry (IHC) on paraffin embedded tissues. Not tested on frozen tissues or Western-Blotting
IHC positive control:Breast, colon or lung adenocarcinoma
Visualization: Cell cytoplasm and membrane
-
آنتی بادیهای ایمونوهیستوشیمی
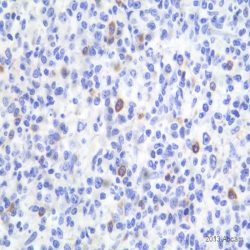
آنتی بادی CD25 (4C9)
Rated 0 out of 5Read moreName: CD25 antibody clone 4C9
Description and aplications: The CD25 molecule, also known as IK-2 receptor alpha, IL2RA, p55, T-cell growth factor receptor (TCGFR) or TAC antigen is an activation antigen present, along with CD4, in regulatory T cells. The gene that controls its expression, with 8 exons and over 25 kb, codes the alpha subunit of the cell surface receptor IL-2 and is located in the chromosome region 10p15.1. The regulatory T cells, since they suppress the activation of autoreactive T cells controlling the immune tolerance, prevent autoimmune diseases and, as negative collateral effects, avoid the destruction of tumor cells by cytotoxic T lymphocytes and act as suppressors of the NK cells. Partial deletions of the CD25 gene are responsible for immunodeficiency 41 (characterized by the association of various lymphoproliferative syndromes with autoimmune diseases) and insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus type 10, a variant of diabetes mellitus type I associated with autoimmune diseases and with typical familial aggregation. In normal tissues, CD25 can be expressed by activated B and T lymphocytes, macrophages and osteoblasts. Some thymocytes, myeloid precursors and oligodendrocytes can also show immunostaining. This molecule is not expressed in normal mastocytes. According to the classification system of the World Health Organization, the main diagnostic criterion for the involvement of bone marrow by systemic mastocytosis (SM) is the presence of dense aggregates (more than 15 cells) of mastocytes. For this reason, the aberrant expression of CD25 as a low affinity receptor for interleukin-2 (IL-2) by neoplastic mast cells is a good diagnostic tool to distinguish them from reactive proliferations of mast cells, and for this reason it has recently become a minor criterion for the diagnosis of SM, where aberrant staining of mastocytes aggregates by anti-CD25 antibody is diagnostic of SM. The anti-CD25 antibody has also been useful for the identification of mastocytes on skin biopsies in the context of urticaria pigmentosa as a predictor of systemic mastocytosis. Additionally, the quantification of regulatory T-cells (Treg) expressing CD25 in the context of hepatocellular carcinoma has been used as an independent predictor of tumor recurrence following liver resection of a previous hepatocellular carcinoma. In addition, the percentage of regulatory T cells FOXP3+ CD25+ infiltrating between melanoma tumor cells and in their periphery is significantly higher in melanomas with recurrent capacity than in their non-recurrent forms.
Finally, CD25 together with CD103 and CD123 is useful for completing the panel of markers of hairy cell leukemia, although the latter two antibodies have greater specificity and sensitivity for this diagnosis than CD25 itself.
Similarly, due to its general low specificity, the CD25 antibody’s positive staining should be evaluated within an antibody panel, not in isolation, and in correlation with the remaining morphological aspects of the lesions analyzed since many B lymphomas, T lymphomas, or even anaplastic large cell lymphoma may present staining against this marker.Composition: anti-CD25 mouse monoclonal antibody obtained from supernatant culture and prediluted in a tris buffered solution pH 7.4 containing 0.375mM sodium azide solution as bacteriostatic and bactericidal.
Intended use: Immunohistochemistry (IHC) on paraffin embedded tissues. Not tested on frozen tissues or Western-Blotting
Immunogen: Recombinant protein corresponding to the external domain of the human IL-2R
-
آنتی بادیهای ایمونوهیستوشیمی
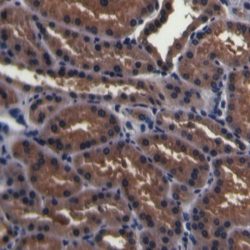
آنتی بادی PSMA (EP192)
Rated 0 out of 5Read moreName: Prostate Specific Membrane Antigen Antibody clone EP192
Description and aplications: Glutamate Carboxypeptidase 2 (GCP2) or folate hydrolase 1 (FOLH1), also known as prostate specific membrane antigen (PSM or PSMA), is a type II homodimeric transmembrane protein of 750 amino acids of approximately 100 kDA of molecular mass that is encoded by the FOLH1 gene, which is located in the chromosome region 11p11.12. The FOLH1 protein is functionally characterized by an intense folase-hydrolase and dipeptidase activity on N-acetylated wastes of tri-alpha-glutamate peptides, regulating the absorption of folate in the intestine and the excitatory neurotransmission associated with the hydrolysis of the neuropeptide N-acetylaspartylglutamate in the CNS (central nervous system). In pathologic circumstances in the CNS, an excess of function of FOLH1 causes an excitotoxic effect due to the generation of high levels of glutamate that, as a consequence, leads to the death of motor cells in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in both its sporadic and familial variants. In fact, FOLH1 inhibitors produce protective effects in this type of conditions when the glutamate levels decrease. In normal tissues, the protein is present in large amounts in the prostate epithelium, where it has an unknown function. However, it is known that in tumors that derive from this gland, FOLH1 is involved in the tumor progression. The protein can also be found in the small intestine (brush border), urinary epithelium, kidney, testicle, ovary, uterine tubes, breast, suprarenal gland, liver, esophagus, stomach, colon and brain (mainly brainstem and corpus striatum). In neoplastic tissues, FOLH1 can be present in tumors of the small intestine, brain, kidney, liver, spleen, trachea, spinal cord, and capillary endothelium. In the prostate, the PSMA molecule (FOLH1) can be found in both benign and malignant lesions, although in neoplasms, an increase in the intensity and number of stained cells in direct relation to the aggressiveness of the carcinoma can be observed. Therefore, it is also indirectly correlated with the expression of androgen receptors. In comparison with the prostate specific antigen (PSA), the determination of PSMA in tumors is a more sensitive procedure but less specific. Therefore, PSMA antibody is used in the diagnosis and prognosis of prostate tumors and as a possible marker for various neurodegenerative brain diseases such as schizophrenia and Alzheimer’s and Huntington’s diseases. Likewise, the Indium-labeled 7E11 anti-FOLH1 monoclonal antibody (ProstaScint®) is used for the diagnostic imaging of primary and metastatic prostate tumors.
Composition: Anti-human PSMA rabbit monoclonal antibody purified from culture supernatant, filtered, sterilized and prepared in 10mM PBS, pH 7.4, with 0.2% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide
Intended use: Immunohistochemistry (IHC) on paraffin embedded tissues. Not tested on frozen tissues or Western-Blotting
Immunogen: Synthetic peptide corresponding to the human PSMA.
-
آنتی بادیهای ایمونوهیستوشیمی
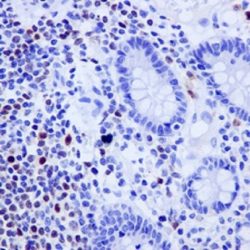
آنتی بادی Oct2 (PT2)
Rated 0 out of 5Read moreName: Mouse anti-human OCT-2 Monoclonal Antibody clone PT2
Description and aplications: Transcription factors Oct1 and OCT2 are located on chromosomal regions 1q22-q23 and 19 respectively, and belong to the POU family homeobox genes that bind DNA in monomeric and dimeric several configurations. Depending on the DNA sequence with which the dimers are joined, they are aligned in an accessible (MORE sequence) or inaccessible (PORE sequence) configuration for specific performance of the cofactor OBF1 of the B lymphocytes (Ocab, BOB1). OCT2 is an important element for the regulation of cellular and tissue specific transcription as well as transcription of numerous genes controllers. While Oct1 expression is an ubiquitous, OCT2 nuclear transcription factor expression is restricted to normal neurons of the central nervous system and B lymphocytes. This antibody recognizes the transcription factor Oct-2 of human, murine and rat origin and does not crossreact with other transcription factors. Oct-2 is expressed in normal B lymphocytes with greater intensity in the germinal center of lymphoid follicles. Small lymphocytes of the mantle areas have lower intensity and a small number of lymphocytes of the marginal and interfollicular areas also show intense nuclear staining. Since the expression of Oct-2 is related to the state of maturation of B cells, the antibody is primarily useful in the identification of B cell lymphomas originated in the germinal centre. In contrast to the L & H cells of lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin’s disease (HD), the Reed-Sternberg (RS) cells of HD classical type are unable to transcribe immunoglobulins due to the absence of Oct-2. Therefore Oct-2 has been considered a new marker to identify and differentiate the L & H from HRS cells in Hodgkin’s disease. Immunostaining for Oct-2 is present intensively in nodular lymphocyte-predominant HD and with less intensity in the variants of the classic HD (HD rich in lymphocytes, HD mixed cellularity, HD nodular sclerosis) numerous cases being Oct-2 negative. In the nervous system it is considered that the expression of Oct-2 plays an important role in female sexual maturation in mammals regulated by the hypothalamus and the regulation of the latency period after infection with herpesvirus.
Composition: anti-human OCT2 mouse monoclonal antibody purified from serum and prepared in 10mM PBS, pH 7.4, with 0.2% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide
Immunogen: full length Oct-2 of human origin
Species reactivity: In vitro diagnostics in humans. Not tested in other species
-
پروبهای فیش
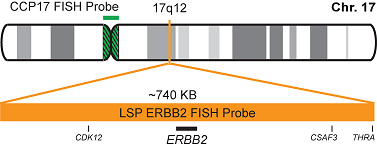
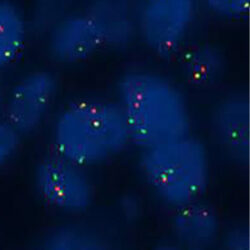
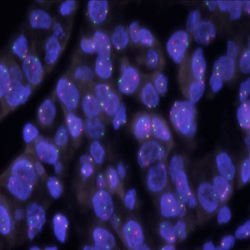
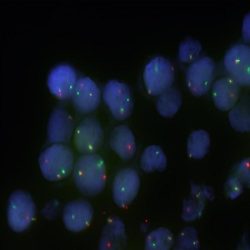
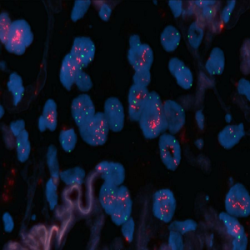
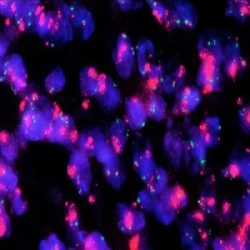
پروب فیش HER2/CEN17 FISH Probe
Rated 0 out of 5Read moreINTRODUCTION: HER2, also known as epidermal growth factor receptor 2, neu, ERBB2 or CD340 is a proto-oncogene located in the human chromosome 17, band 21 that code a transmembrane glycoprotein (p185) with tyrosine-kinase activity. Because of its interaction and similarity to EGFR and other members of the epidermal growth factor receptor family, HER2 takes part in the differentiation of some cell-lines during embryogenesis after the interaction between mesenchyme–epithelium-neuroectoderm. It also has an influence on the migration, differentiation and interaction between numerous cells.
The overexpression of HER2 has been proven in over 20% of adenocarcinomas of different locations, including lung, uterus, gastrointestinal and urinary tract, breast and skin appendages in different studies. In case of breast and stomach cancers, the overexpression of this oncoprotein, which is associated with a worse prognosis, is related to the gene amplification and it is subsidiary of responding to treatment anti HER2 with Trastuzumab (Herceptin), the humanized monoclonal antibody able to block this growth receptor and for which purpose, similar results have been obtained in malignant neoplasias, such as ovarian, stomach and salivary gland carcinomas.
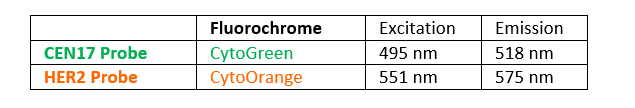
INTENDED USE: The HER2 FISH probe is designed to detect the number of copies of the gen ERBB2 (Her2/neu) in the 17q12 chromosome region. The probe CEN17 is designed to detect an alpha-satellite sequence of DNA located in the 17p11.1 region and allows identifying and counting the number of copies of chromosome 17.PROBE DESCRIPTION: The Her2 FISH Probe labeled with the CytoOrange fluorochrome covers a chromosomal region which includes the entire ERBB2 gene. The CCP17 FISH Probe labeled with the CytoGreen fluorochrome is covering the alpha satellite region of the centromere of the chromosome 17 and is designed as a control to determine the number of copies per cell of the chromosome 17.
-
پروبهای فیش
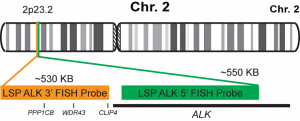
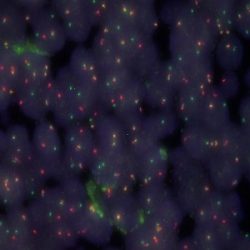
پروب فیش ALK Break Apart FISH Probe
Rated 0 out of 5Read moreINTRODUCTION:Rearrangements of the ALK gene (also known as CD246 or NBLST3), initially discovered in anaplastic large cell lymphoma, have also been found in many types of malignant tumors, including B and T-cell lymphomas, plasmacytomas, neuroblastomas, esophageal, breast, kidney, colon, thyroid and lungcarcinomas, among others.A significant percentage of cases of non-small cell lung cancer (3-13%) show abnormalities of the ALK gene and are likely to targeted treatments withspecific tyrosine kinases inhibitors that show significant benefits as compared to conventional chemotherapy.
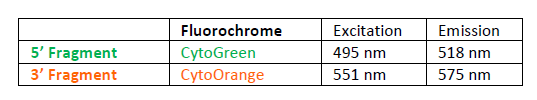
INTENDED USE: The ALK Break Apart FISH probe is designed to detect rearrangements in the ALK human gene located in the band of the chromosome 2p23.2. Aside from detecting breaks that can lead to translocation of parts of the gene, to its inversion or to its fusion with other genes, the probe can also be used to identify other aberrations of ALK such as deletions or amplifications.PROBE DESCRIPTION:The 5’ centromeric fragment of the ALK Break Apart FISH probe labeled with the fluorochrome CytoGreen covers the 5’ and central sequences of the ALK gene. The 3’ telomeric fragment of the ALK Break apart FISH probe labeled with CytoOrange covers the 3’ end and the contiguous neighboring region. Both probes are designed to detect sequences in both sides in a mutual cut-off point that is located within the ALK gene.
-
پروبهای فیش
پروب فیش ROS1 Break Apart FISH Probe
Rated 0 out of 5Read moreINTRODUCTION:
Rearrangements and abnormal expression of the ROS1 gene (also known as ROS, MCF3 or c-ros-1) have been described in approximately 1-2% of non-small cell lung carcinomas and other types of tumors. The detection of the ROS1 rearrangement in lung tumors allows applying a treatment with specific inhibitors in patients, which has shown a greater survival as compared to conventional chemotherapy.
INTENDED USE:
The ROS1 Break Apart FISH probe is designed to detect rearrangements in the ROS1 human gene located in the band of the chromosome 6q22.1. Aside from detecting breaks that can lead to translocation of parts of the gene, to its inversion or to its fusion with other genes, the probe can also be used to identify other aberrations of ROS1 such as deletions or amplifications.
PROBE DESCRIPTION:
The 5’ telomeric fragment of the ROS1 Break Apart FISH probe labeled with the fluorochrome CytoGreen covers the 5’ portion (beginning) of the ROS1 gene and some adjacent genomic sequences. The 3’ centromeric fragment of the ROS1 Break apart FISH probe labeled with CytoOrange covers the 3’ part (end) and the adjacent and inferior sequences of the gene.Both probes are flanking sequences in the ROS1 gene, in which variable cut-off points have been observed.

-
پروبهای فیش
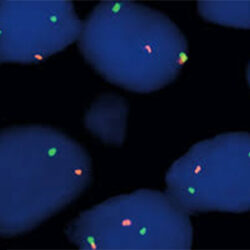
پروب فیش CCND1 Break Apart FISH Probe
Rated 0 out of 5Read moreINTRODUCTION: Rearrangements and abnormal expression of the CCND1 gene (also known as BCL1, PRAD1, U21B31 or D11S287E) have been described in several types of hematological malignancies such as follicular mantle lymphoma [t(11;14) CCND1/IGH] or some cases of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Although up to 15-20% of the malignant myelomas usually show Cyclin D nuclear expression, these cases do not have CCND1 gene translocation. On the other hand, there are cases of cyclin D1-negative mantle cell lymphoma and only the detection of the CCND1 gene translocation after a hybridization study can establish a diagnosis.
INTENDED USE: The CCND1 Break Apart FISH probe is designed to detect rearrangements in the CCND1 human gene located in the band of the chromosome 11q13.3. Aside from detecting breaks that can lead to translocation of parts of the gene, to its inversion or to its fusion with other genes, the probe can also be used to identify other aberrations of CCND1 such as deletions or amplifications.
PROBE DESCRIPTION: The 3’ telomeric fragment of the CCMD1 Break Apart FISH probe labeled with the fluorochrome CytoOrange covers some genomic sequences adjacent to the 3’ portion (beginning) of the CCND1. The 5’ centromeric fragment of the CCND1 Break apart FISH probe labeled with CytoGreen covers the sequences adjacent to the gene’s 3’ end. Both probes are flanking sequences of the CCND1 gene, in which variable cut-off points have been observed.

-
پروبهای فیش
پروب فیش BCL2 Break Apart FISH Probe
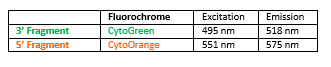
Rated 0 out of 5Read moreINTRODUCTION:Rearrangements and abnormal expression of the BCL2 gene (also known as Bcl-2 or PPP1R50), are usually located in the follicular lymphoma, but they are also present in many other types of hematological and solid neoplasias. A particularly usual rearrangement is a reciprocal translocation of the IGH locus of the chromosome 14, present in up to 90% of follicular lymphomas and in up to 30% of diffuse large B-cell lymphomas.
INTENDED USE:The BCL2 Break Apart FISH probe is designed to detect rearrangements in the BCL2 human gene located in the chromosome band 18q21.33. Aside from detecting breaks (break-apart/split) that can lead to translocation of parts of the gene, to its inversion or to its fusion with other genes, the probe can also be used to identify other aberrations of BCL2 such as deletions or amplifications.
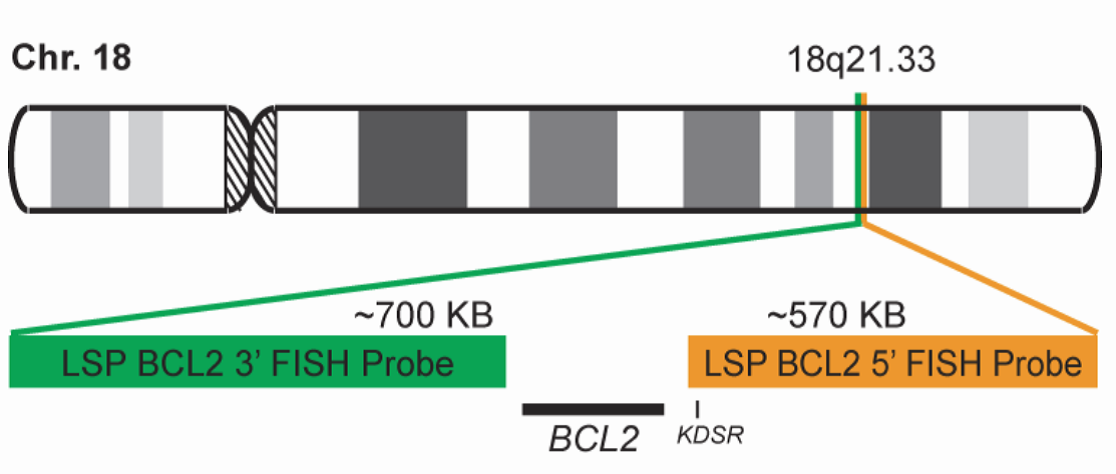
PROBE DESCRIPTION:The 5’ telomeric fragment of the BCL2 Break Apart FISH probe labeled with the fluorochrome CytoOrange covers sequences adjacent to the 5’ portion (beginning) of the BCL2. The 3’ centromeric fragment of the BCL2 Break apart FISH probe labeled with CytoGreen covers some distal sequences (3’ end) of the gene. Both marked loci are flanking sequences of the BCL2 gene, in which numerous cut-off points have been observed.
-
پروبهای فیش
پروب فیش BCL6 Break Apart FISH Probe
Rated 0 out of 5Read moreINTRODUCTION: Rearrangements of the BCL6 gene (also known as BCL5, LAZ3, BCL6A, ZNF51 or ZBTB27) have been described in lymphomas and B-cell leukemias. BCL6 is also unregulated in cases of multiple myeloma and several types of solid tumors. More than 30 different genes have been described as translocation pairs. In practice, the presence of the BCL6 translocation may have diagnostic value in follicular lymphomas grade 3B with negative BCL2 translocation, while in diffuse large B-cell lymphomas, along with BCL2 and MYC translocations, it presents a prognostic and therapeutic value.
INTENDED USE: The BCL6 Break Apart FISH probe is designed to detect rearrangements in the BCL6 human gene located in the chromosome band 3q27.3. Aside from detecting breaks that can lead to translocation of parts of the gene, to its inversion or to its fusion with other genes, the whole probe can also be used to identify other aberrations of BCL6, such as deletions or amplifications.
PROBE DESCRIPTION: The 5’ telomeric fragment of the BCL6 Break Apart FISH probe labeled with the fluorochrome CytoOrange covers some sequences adjacent to the 5’ portion (beginning) of the BCL6. The 3’ centromeric fragment of the BCL6 Break apart FISH probe labeled with CytoGreen covers some distal sequences (3’ end) of the gene. Both loci are flanking sequences of the BCL6 gene, in which numerous cut-off points have been observed.

-
پروبهای فیش
پروب فیش IGH Break Apart FISH Probe
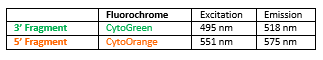
Rated 0 out of 5Read moreINTRODUCTION: Rearrangements involving the IGH locus (or immunoglobulin heavy locus) have been observed in many types of leukemias and lymphomas. It represents the prototype for translocations in B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphomas, in which it has been detected in up to 50% of the cases, whereas reciprocal and specific translocations with different chromosomal loci have been characterized and considered as pathognomonic for different histological subtypes.
INTENDED USE: The IGH Break Apart FISH probe is designed to detect rearrangements in the human IGH locus located in the chromosome band 14q32.33. Aside from detecting breaks that can lead to translocation of parts of the locus, to its inversion or to its fusion with other genes, the probe can also be used to identify other aberrations of IGH such as deletions or amplifications.
PROBE DESCRIPTION: The telomeric 5’ Fragment of the IGH Break Apart FISH probe labeled with the fluorochrome CytoOrange covers the 5’ portion and the center of the locus of the IGH gene, whereas the centromeric 3’ fragment of the IGH Break Apart FISH probe labeled with CytorGreen covers some distal sequences (3’ end) of the gene.Both loci are flanking sequences of the BCL2 gene, in which numerous cut-off points have been observed.
-
پروبهای فیش
پروب فیش MYC Break Apart FISH Probe
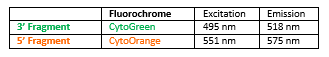
Rated 0 out of 5Read moreINTRODUCTION: Rearrangements and abnormal expression of the MYC gene (also known as MRTL, MYCC, c-Myc or bHLHe39) has been described in Burkitt lymphoma, in which its positivity has diagnostic utility in a clinical, morphological and immunohistochemical context. On the other hand, diffuse large B-cell or non-classifiable lymphoma, the MYC translocation shows a prognostic value and dictates a more aggressive treatment of the neoplasia. On the other hand, along with the determination of the BCL2 and BCL6 genes translocation, it has the purpose of establishing the double or triple-hit character of the neoplasia. Other hematological neoplasias, myelomas, as well as breast, cervical, colon or ovarian tumors, among others, can show MYC translocation.
INTENDED USE: The MYC Break Apart FISH probe is designed to detect rearrangements in the MYC human gene located in the chromosome band 8q24.21. Aside from detecting breaks that can lead to translocation of parts of the gene, to its inversion or to its fusion with other genes, the probe can also be used to identify other aberrations of MYC such as deletions or amplifications.
PROBE DESCRIPTION: The 5’ centromeric fragment of the MYC Break Apart FISH probe labeled with the fluorochrome CytoOrange covers genomic sequences adjacent to the 5’ portion (beginning) of the MYC gene. The 3’ telomeric fragment of the MYC Break apart FISH probe labeled with CytoGreen covers some distal sequences (3’ end) of the gene.Both loci are flanking sequences of the MYC gene, in which variable cut-off points have been observed.
-
پروبهای فیش
پروب فیش MET/CEN7 FISH Probe
Rated 0 out of 5Read moreINTRODUCTION: The rearrangements and the abnormal expression of the MET gene (also known as HGFR, AUTS9, RCCP2 or c-Met) have been described in hereditary and sporadic renal tumors and other types of tumors. The amplification of the MET gene has been detected in lung, breast, gastrointestinal and prostate carcinomas as well as in gliomas and melanomas, among others. In these tumors, the amplification of the gene is a negative prognostic factor and, in some cases, it is associated with resistance to the treatment.
INTENDED USE: The MET/CEN7 FISH probe is designed to detect amplifications of the MET human gene located in the band of the chromosome 7q31.2, in relation to the centromere of the Chromosome 7.
PROBE DESCRIPTION: The MET FISH probe labeled with the CytoOrange fluorochrome covers a chromosome region that includes the whole MET gene. The CEN7 FISH probe labeled with the CytoGreen fluorochrome is derived from the alpha satellite region of the centromere of the chromosome 7 and is designed as a control to determine the number of copies of the chromosome 7 per cell.

-
پروبهای فیش
پروب فیش MDM2/CEN12 FISH Probe
Rated 0 out of 5Read moreINTRODUCTION: An abnormal expression of the MDM2 gene (also known as MDM2, hdm2 or ACTFS) has been described, generally associated by amplification of the same with a 7% of the human neoplastic processes. The neoplasms that more frequently show MDM2 gene amplification are atypical lipomatous tumors/well-differentiated liposarcomas, undifferentiated liposarcomas, intimal sarcomas and low-grade osteosarcomas (parosteal/intramedullary).
INTENDED USE: The MDM2/CEN12 FISH probe is designed to analyze the MDM2 human gene located in the band of the chromosome 12q15, in relation to the centromere of the Chromosome 12.
PROBE DESCRIPTION: The MDM2 FISH Probe labeled with the CytoOrange fluorochrome covers a chromosome region that includes the whole MDM2 gene. The CCP12 FISH Probe labeled with the CytoGreen fluorochrome is derived from the alpha satellite region of the centromere of the chromosome 12 and is designed as a control to determine the number of copies per cell of the chromosome 12.

-
پروبهای فیش
پروب فیش MALT1 Break Apart FISH Probe
Rated 0 out of 5Read moreINTRODUCTION: Rearrangements and abnormal expression of the MALT1 gene (also known as MLT, MLT1 or IMD12), in B-cell lymphomas and other malignant diseases have been described. There are two types of translocations that involve the MALT1 gene described in lymphomas: t(11;18)(q21;q21.32) that involves BIRC3/MALT1 (the most frequent) and t(14;18)(q32;q21.32) of the IGH/MALT1 genes. Up to 33% of the mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue B-cell lymphoma (MALT-type B-cell lymphoma) present translocation, whereas the vast majority of primary MALT lymphomas in lymph node or spleen are negative.
INTENDED USE: The MALT1 Break Apart FISH probe is designed to detect rearrangements in the MALT1 human gene located in the band of the chromosome 18q21.32. Aside from detecting breaks that can lead to translocation of parts of the gene, to its inversion or to its fusion with other genes, the probe can also be used to identify other aberrations of MALT1 such as deletions or amplifications.
PROBE DESCRIPTION: The 5’ centromeric fragment of the MALT1 Break Apart FISH probe labeled with the fluorochrome CytoOrange covers the 5’ portion (beginning) of the MALT1 gene and some adjacent genomic sequences. The 3’ telomeric fragment of the MALT1 Break apart FISH probe labeled with CytoGreen covers the 3’ part (end) and the adjacent and inferior sequences of the gene. Both probes are flanking sequences of the MALT1 gene, in which variable cut-off points have been observed.

-
پروبهای فیش
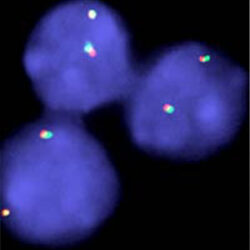
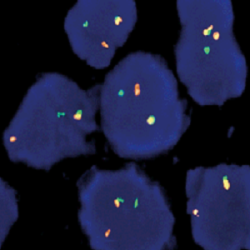
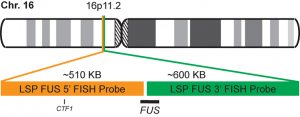
پروب فیش FUS Break Apart FISH Probe
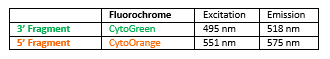
Rated 0 out of 5Read moreINTRODUCTION: Rearrangements and abnormal expression of the FUS gene (also known as TLS, ALS6, ETM4, FUS1, POMP75 or HNRNPP2) have been described in the alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma, prostate carcinoma and other types of tumors such as myxoid liposarcoma, low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma or some cases of Ewing’s sarcoma.
INTENDED USE: The FUS Break Apart FISH probe is designed to detect rearrangements in the FUS human gene located in the band of the chromosome 16p11.2. Aside from detecting breaks that can lead to the translocation of parts of the gene, to its inversion or to its fusion with other genes, the probe can also be used to identify other aberrations of FUS such as deletions or amplifications.
PROBE DESCRIPTION: The 5’ telomeric fragment of the FUS Break Apart FISH probe labeled with the fluorochrome CytoOrange covers the 5’ portion (beginning) of the FUS gene and some adjacent genomic sequences. The 3’ centromeric fragment of the FUS Break apart FISH probe labeled with CytoGreen covers the center and the 3’ part (end) as well as the distal sequences of the gene. Both probes are flanking sequences in the FUS gene, in which variable cut-off points have been observed.
-
پروبهای فیش
پروب فیش EWSR1 Break Apart FISH Probe
Rated 0 out of 5Read moreINTRODUCTION: The rearrangements and abnormal expression of the EWSR1 gene (also known as EWS or bK984G1.4) have been described in numerous soft-tissue lesions. Depending on the other gene involved in the reciprocal translocation, the break of the EWSR1 gene can be involved in the pathogenesis of the desmoplastic small-round-cell tumor, Ewing’s sarcoma/PNET, myxoid chondrosarcoma, soft-tissue myoepithelial tumor, myxoid liposarcoma, clear-cell sarcoma (soft-tissue melanoma), pulmonary myxoid sarcoma or hyalinizing clear cell carcinoma of salivary gland, among others. Thus, the presence of the EWSR1 gene rearrangement should be indicative, and the final diagnosis should be made by corroborating morphological, immunohistochemical and sometimes radiological facts.
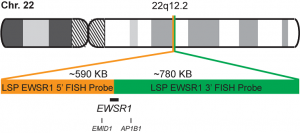
INTENDED USE: The EWSR1 Break Apart FISH probe is designed to detect rearrangements in the EWSR1 human gene located in the band of the chromosome 22q12.2. Aside from detecting breaks that can lead to translocation of parts of the gene, to its inversion or to its fusion with other genes, the probe can also be used to identify other aberrations of EWSR1 such as deletions or amplifications.
PROBE DESCRIPTION: The 5’ centromeric fragment of the EWSR1 Break Apart FISH probe labeled with the fluorochrome CytoOrange covers the 5’ portion (beginning) of the EWSR1 gene and some adjacent genomic sequences. The 3’ telomeric fragment of the EWSR1 Break apart FISH probe labeled with CytoGreen covers the 3’ part (end) as well as the adjacent and inferior sequences of the gene. Both probes are flanking sequences in the EWSR1 gene, in which variable cut-off points have been observed.